Annotation, phylogeny and expression analysis of the nuclear factor Y gene families in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris)
- PMID: 25642232
- PMCID: PMC4294137
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00761
Annotation, phylogeny and expression analysis of the nuclear factor Y gene families in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris)
Abstract
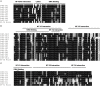
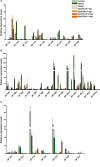
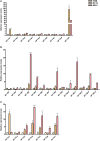
In the past decade, plant nuclear factor Y (NF-Y) genes have gained major interest due to their roles in many biological processes in plant development or adaptation to environmental conditions, particularly in the root nodule symbiosis established between legume plants and nitrogen fixing bacteria. NF-Ys are heterotrimeric transcriptional complexes composed of three subunits, NF-YA, NF-YB, and NF-YC, which bind with high affinity and specificity to the CCAAT box, a cis element present in many eukaryotic promoters. In plants, NF-Y subunits consist of gene families with about 10 members each. In this study, we have identified and characterized the NF-Y gene families of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris), a grain legume of worldwide economical importance and the main source of dietary protein of developing countries. Expression analysis showed that some members of each family are up-regulated at early or late stages of the nitrogen fixing symbiotic interaction with its partner Rhizobium etli. We also showed that some genes are differentially accumulated in response to inoculation with high or less efficient R. etli strains, constituting excellent candidates to participate in the strain-specific response during symbiosis. Genes of the NF-YA family exhibit a highly structured intron-exon organization. Moreover, this family is characterized by the presence of upstream ORFs when introns in the 5' UTR are retained and miRNA target sites in their 3' UTR, suggesting that these genes might be subjected to a complex post-transcriptional regulation. Multiple protein alignments indicated the presence of highly conserved domains in each of the NF-Y families, presumably involved in subunit interactions and DNA binding. The analysis presented here constitutes a starting point to understand the regulation and biological function of individual members of the NF-Y families in different developmental processes in this grain legume.
Keywords: CCAAT box; gene regulation; legumes; nodulation; symbiosis; transcription factors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Phylogenetically Conserved Group of Nuclear Factor-Y Transcription Factors Interact to Control Nodulation in Legumes.Plant Physiol. 2015 Dec;169(4):2761-73. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01144. Epub 2015 Oct 2. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26432878 Free PMC article.
-
The PvNF-YA1 and PvNF-YB7 Subunits of the Heterotrimeric NF-Y Transcription Factor Influence Strain Preference in the Phaseolus vulgaris-Rhizobium etli Symbiosis.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Feb 28;10:221. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00221. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 30873199 Free PMC article.
-
A C subunit of the plant nuclear factor NF-Y required for rhizobial infection and nodule development affects partner selection in the common bean-Rhizobium etli symbiosis.Plant Cell. 2010 Dec;22(12):4142-57. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.079137. Epub 2010 Dec 7. Plant Cell. 2010. PMID: 21139064 Free PMC article.
-
Plant NF-Y transcription factors: Key players in plant-microbe interactions, root development and adaptation to stress.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017 May;1860(5):645-654. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.11.007. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017. PMID: 27939756 Review.
-
The Arabidopsis thaliana Nuclear Factor Y Transcription Factors.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jan 10;7:2045. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.02045. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28119722 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of NF-Y gene family in walnut (Juglans regia L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Oct 23;18(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1459-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30352551 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of the NF-Y gene family in grape (vitis vinifera L.).BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 11;17(1):605. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2989-3. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27516172 Free PMC article.
-
Gene structure, expression pattern and interaction of Nuclear Factor-Y family in castor bean (Ricinus communis).Planta. 2018 Mar;247(3):559-572. doi: 10.1007/s00425-017-2809-2. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Planta. 2018. PMID: 29119268
-
NIPK, a protein pseudokinase that interacts with the C subunit of the transcription factor NF-Y, is involved in rhizobial infection and nodule organogenesis.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 21;13:992543. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.992543. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36212340 Free PMC article.
-
CONSTANS Imparts DNA Sequence Specificity to the Histone Fold NF-YB/NF-YC Dimer.Plant Cell. 2017 Jun;29(6):1516-1532. doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00864. Epub 2017 May 19. Plant Cell. 2017. PMID: 28526714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilar O. M., Lopez M. V., Riccillo P. M., Gonzalez R. A., Pagano M., Grasso D. H., et al. (1998). Prevalence of the Rhizobium etli-like allele in genes coding for 16S rRNA among the indigenous rhizobial populations found associated with wild beans from the Southern Andes in Argentina. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 3520–3524. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Battaglia M., Rípodas C., Clúa J., Baudin M., Aguilar O. M., Niebel A., et al. . (2014). A nuclear factor Y interacting protein of the GRAS family is required for nodule organogenesis, infection thread progression, and lateral root growth. Plant Physiol. 164, 1430–1442. 10.1104/pp.113.230896 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

