Targeting the extrinsic apoptotic pathway in cancer: lessons learned and future directions
- PMID: 25642709
- PMCID: PMC4319431
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI80420
Targeting the extrinsic apoptotic pathway in cancer: lessons learned and future directions
Abstract
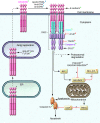
Apoptosis is a metazoan process of controlled cell elimination that plays critical roles in embryonic development and adult tissue homeostasis. Apoptosis dysregulation contributes to several important diseases, including cancer. Two distinct yet interconnected signaling pathways control apoptosis by activating a core intracellular machinery of death proteases called caspases. The intrinsic apoptotic pathway engages caspases via members of the BCL-2 protein family and the mitochondria in reaction to severe cellular damage or stress. The extrinsic pathway activates caspases via cell-surface death receptors, which respond to cognate death ligands expressed on immune-effector cells. Tumor cells can acquire various apoptosis-evasion mechanisms; nevertheless, the transformed state of these cells makes them uniquely susceptible to apoptosis reactivation if resistance is circumvented. Molecular approaches to reengage the apoptotic pathways in cancer have been underway for over two decades. Gratifyingly, BCL-2 antagonists - which drive the intrinsic pathway - are beginning to bear clinical fruit. In contrast, clinical attempts to stimulate the extrinsic pathway with proapoptotic receptor agonists (PARAs) have been disappointing, despite compelling preclinical efficacy with this class of agents. Here, I discuss some of the possible reasons for this translational discrepancy and suggest strategies to overcome it with the next generation of PARAs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Can targeting apoptosis resolve the cancer saga?Future Oncol. 2005 Jun;1(3):339-49. doi: 10.1517/14796694.1.3.339. Future Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16556008 Review.
-
Overcoming resistance of cancer cells to apoptosis.J Cell Physiol. 2003 Jul;196(1):9-18. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10256. J Cell Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12767037 Review.
-
Role of Bcl-2 in tumour cell survival and implications for pharmacotherapy.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;64(12):1695-702. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2012.01526.x. Epub 2012 Apr 25. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23146031 Review.
-
Cancer-specific toxicity of apoptin is independent of death receptors but involves the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and the release of mitochondrial cell-death mediators by a Nur77-dependent pathway.J Cell Sci. 2005 Oct 1;118(Pt 19):4485-93. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02580. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16179607
-
Cell type specific involvement of death receptor and mitochondrial pathways in drug-induced apoptosis.Oncogene. 2001 Mar 1;20(9):1063-75. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204141. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11314043
Cited by
-
Yiqi Chutan Tang Reduces Gefitinib-Induced Drug Resistance in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Targeting Apoptosis and Autophagy.Cytometry A. 2020 Jan;97(1):70-77. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.23869. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Cytometry A. 2020. PMID: 31411813 Free PMC article.
-
In silico evaluation of apoptogenic potential and toxicological profile of triterpenoids.Indian J Pharmacol. 2019 May-Jun;51(3):181-207. doi: 10.4103/ijp.IJP_90_18. Indian J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31391686 Free PMC article.
-
Poxviral Strategies to Overcome Host Cell Apoptosis.Pathogens. 2020 Dec 23;10(1):6. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10010006. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 33374867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical synthetic approaches to mimic the TRAIL: promising cancer therapeutics.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Aug 1;15(11):3639-51. doi: 10.1039/d4md00183d. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39246747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Relevance of Ghrelin in Programmed Cell Death and Its Application in Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 8;24(24):17254. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417254. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139082 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

