Protein Arginine Deiminases and Associated Citrullination: Physiological Functions and Diseases Associated with Dysregulation
- PMID: 25642720
- PMCID: PMC4520219
- DOI: 10.2174/1389450116666150202160954
Protein Arginine Deiminases and Associated Citrullination: Physiological Functions and Diseases Associated with Dysregulation
Abstract
Human proteins are subjected to more than 200 known post-translational modifications (PTMs) (e.g., phosphorylation, glycosylation, ubiquitination, S-nitrosylation, methylation, Nacetylation, and citrullination) and these PTMs can alter protein structure and function with consequent effects on the multitude of pathways necessary for maintaining the physiological homeostasis. When dysregulated, however, the enzymes that catalyze these PTMs can impact the genesis of countless diseases. In this review, we will focus on protein citrullination, a PTM catalyzed by the Protein Arginine Deiminase (PAD) family of enzymes. Specifically, we will describe the roles of the PADs in both normal human physiology and disease. The development of PAD inhibitors and their efficacy in a variety of autoimmune disorders and cancer will also be discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest.
Figures
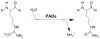


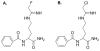
References
-
- Rogers GE, Simmonds DH. Content of citrulline and other aminoacids in a protein of hair follicles. Nature. 1958;182(4629):186–7. - PubMed
-
- Rus’d AA, Ikejiri Y, Ono H, et al. Molecular cloning of cDNAs of mouse peptidylarginine deiminase type I, type III and type IV, and the expression pattern of type I in mouse. Eur J Biochem. 1999;259(3):660–9. - PubMed
-
- Ishigami A, Ohsawa T, Asaga H, Akiyama K, Kuramoto M, Maruyama N. Human peptidylarginine deiminase type II: molecular cloning, gene organization, and expression in human skin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2002;407(1):25–31. - PubMed
-
- Chavanas S, Méchin MC, Takahara H, et al. Comparative analysis of the mouse and human peptidylarginine deiminase gene clusters reveals highly conserved non-coding segments and a new human gene, PADI6. Gene. 2004;330:19–27. - PubMed
-
- Fujisaki M, Sugawara K. Properties of peptidylarginine deiminase from the epidermis of newborn rats. J Biochem. 1981;89(1):257–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
