Pacemaker activity of the human sinoatrial node: an update on the effects of mutations in HCN4 on the hyperpolarization-activated current
- PMID: 25642760
- PMCID: PMC4346881
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms16023071
Pacemaker activity of the human sinoatrial node: an update on the effects of mutations in HCN4 on the hyperpolarization-activated current
Abstract
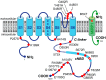
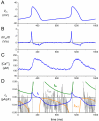
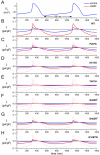
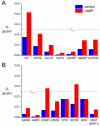
Since 2003, several loss-of-function mutations in the HCN4 gene, which encodes the HCN4 protein, have been associated with sinus node dysfunction. In human sinoatrial node (SAN), HCN4 is the most abundant of the four isoforms of the HCN family. Tetramers of HCN subunits constitute the ion channels that conduct the hyperpolarization-activated "funny" current (If), which plays an important modulating role in SAN pacemaker activity. Voltage-clamp experiments on HCN4 channels expressed in COS-7, CHO and HEK-293 cells, as well as in Xenopus oocytes have revealed changes in the expression and kinetics of mutant channels, but the extent to which especially the kinetic changes would affect If flowing during a human SAN action potential often remains unresolved. In our contribution to the Topical Collection on Human Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Disease Diagnostics, we provide an updated review of the mutation-induced changes in the expression and kinetics of HCN4 channels and provide an overview of their effects on If during the time course of a human SAN action potential, as assessed in simulated action potential clamp experiments. Future research may solve apparent inconsistencies between data from clinical studies and data from in vitro and in silico experiments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pacemaker activity of the human sinoatrial node: effects of HCN4 mutations on the hyperpolarization-activated current.Europace. 2014 Mar;16(3):384-95. doi: 10.1093/europace/eut348. Europace. 2014. PMID: 24569893 Review.
-
HCN4 and arrhythmias: Insights into base mutations.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2025 Jan-Jun;795:108534. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2025.108534. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2025. PMID: 39922561 Review.
-
In Vitro Analyses of Novel HCN4 Gene Mutations.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(3):1197-1207. doi: 10.1159/000493301. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30196304
-
Heteromeric HCN1-HCN4 channels: a comparison with native pacemaker channels from the rabbit sinoatrial node.J Physiol. 2003 Jun 1;549(Pt 2):347-59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.027698. Epub 2003 Apr 17. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12702747 Free PMC article.
-
HCN4 pacemaker channels attenuate the parasympathetic response and stabilize the spontaneous firing of the sinoatrial node.J Physiol. 2018 Mar 1;596(5):809-825. doi: 10.1113/JP275303. Epub 2018 Feb 6. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29315578 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Computational analysis of the human sinus node action potential: model development and effects of mutations.J Physiol. 2017 Apr 1;595(7):2365-2396. doi: 10.1113/JP273259. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28185290 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Potential Targets of Shenxian-Shengmai Oral Liquid in Treating Sick Sinus Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Nov 12;12(12):10517-10534. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4587. eCollection 2024 Dec. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39723092 Free PMC article.
-
Palmitoylation regulates the magnitude of HCN4-mediated currents in mammalian cells.Front Physiol. 2023 Apr 13;14:1163339. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1163339. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37123274 Free PMC article.
-
An anchor-tether 'hindered' HCN1 inhibitor is antihyperalgesic in a rat spared nerve injury neuropathic pain model.Br J Anaesth. 2023 Oct;131(4):745-763. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2023.06.067. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Br J Anaesth. 2023. PMID: 37567808 Free PMC article.
-
The Functional Role of Hyperpolarization Activated Current (I f) on Cardiac Pacemaking in Human vs. in the Rabbit Sinoatrial Node: A Simulation and Theoretical Study.Front Physiol. 2021 Aug 19;12:582037. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.582037. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34489716 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

