Cytosolic HMGB1 controls the cellular autophagy/apoptosis checkpoint during inflammation
- PMID: 25642769
- PMCID: PMC4362239
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI76344
Cytosolic HMGB1 controls the cellular autophagy/apoptosis checkpoint during inflammation
Abstract
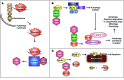
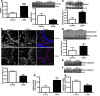
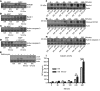
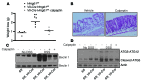
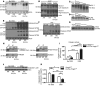
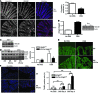
The intracellular protein HMGB1 is released from cells and acts as a damage-associated molecular pattern molecule during many diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); however, the intracellular function of HMGB1 during inflammation is poorly understood. Here, we demonstrated that cytosolic HMGB1 regulates apoptosis by protecting the autophagy proteins beclin 1 and ATG5 from calpain-mediated cleavage during inflammation. Colitis in mice with an intestinal epithelial cell-specific Hmgb1 deletion and patients with IBD were both characterized by increased calpain activation, beclin 1 and ATG5 cleavage, and intestinal epithelial cell (IEC) death compared with controls. In vitro cleavage assays and studies of enteroids verified that HMGB1 protects beclin 1 and ATG5 from calpain-mediated cleavage events that generate proapoptotic protein fragments. Together, our results indicate that HMGB1 is essential for mitigating the extent and severity of inflammation-associated cellular injury by controlling the switch between the proautophagic and proapoptotic functions of beclin 1 and ATG5 during inflammation. Moreover, these studies demonstrate that HMGB1 is pivotal for reducing tissue injury in IBD and other complex inflammatory disorders.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 DK042086/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1F32DK082104/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-42086/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI083375/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK047722/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007090/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK082104/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI083375/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK097268/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK47722/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK097268/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK42086/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK047722/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

