αβ T cell antigen receptor recognition of CD1a presenting self lipid ligands
- PMID: 25642819
- PMCID: PMC7103088
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.3098
αβ T cell antigen receptor recognition of CD1a presenting self lipid ligands
Abstract
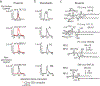
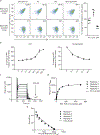
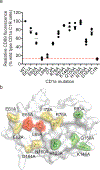
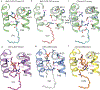
A central paradigm in αβ T cell-mediated immunity is the simultaneous co-recognition of antigens and antigen-presenting molecules by the αβ T cell antigen receptor (TCR). CD1a presents a broad repertoire of lipid-based antigens. We found that a prototypical autoreactive TCR bound CD1a when it was presenting a series of permissive endogenous ligands, while other lipid ligands were nonpermissive to TCR binding. The structures of two TCR-CD1a-lipid complexes showed that the TCR docked over the A' roof of CD1a in a manner that precluded direct contact with permissive ligands. Nonpermissive ligands indirectly inhibited TCR binding by disrupting the TCR-CD1a contact zone. The exclusive recognition of CD1a by the TCR represents a previously unknown mechanism whereby αβ T cells indirectly sense self antigens that are bound to an antigen-presenting molecule.
Figures



References
-
- Eckle SBG, Turner SJ, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. Predisposed αβ T cell antigen receptor recognition of MHC and MHC-I like molecules? Current Opinion in Immunology 2013, 25(5): 653–659. - PubMed
-
- Rossjohn J, Gras S, Miles JJ, Turner SJ, Godfrey DI, McCluskey J. T Cell Antigen Receptor Recognition of Antigen-Presenting Molecules. Annu Rev Immunol 2014, in press. - PubMed
-
- Zinkernagel RM, Doherty PC. Restriction of in vitro T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in lymphocytic choriomeningitis within a syngeneic or semiallogeneic system. Nature 1974, 248(450): 701–702. - PubMed
-
- Brigl M, Brenner MB. CD1: Antigen Presentation and T Cell Function. Annu Rev Immunol 2004, 22: 817–890. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

