IL-1 signaling modulates activation of STAT transcription factors to antagonize retinoic acid signaling and control the TH17 cell-iTreg cell balance
- PMID: 25642823
- PMCID: PMC4790724
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.3099
IL-1 signaling modulates activation of STAT transcription factors to antagonize retinoic acid signaling and control the TH17 cell-iTreg cell balance
Abstract
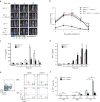
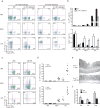
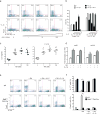
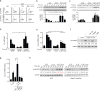
Interleukin 17 (IL-17)-producing helper T cells (TH17 cells) and CD4(+) inducible regulatory T cells (iTreg cells) emerge from an overlapping developmental program. In the intestines, the vitamin A metabolite retinoic acid (RA) is produced at steady state and acts as an important cofactor to induce iTreg cell development while potently inhibiting TH17 cell development. Here we found that IL-1 was needed to fully override RA-mediated expression of the transcription factor Foxp3 and induce protective TH17 cell responses. By repressing expression of the negative regulator SOCS3 dependent on the transcription factor NF-κB, IL-1 increased the amplitude and duration of phosphorylation of the transcription factor STAT3 induced by TH17-polarizing cytokines, which led to an altered balance in the binding of STAT3 and STAT5 to shared consensus sequences in developing T cells. Thus, IL-1 signaling modulated STAT activation downstream of cytokine receptors differently to control the TH17 cell-iTreg cell developmental fate.
Figures


Comment in
-
IL-1 watches the watchmen.Nat Immunol. 2015 Mar;16(3):226-7. doi: 10.1038/ni.3105. Nat Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25689436 No abstract available.
-
All in (IL-) 1?Transplantation. 2015 Nov;99(11):2235-6. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000966. Transplantation. 2015. PMID: 26492049 No abstract available.
References
-
- Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ, Locksley RM, Stockinger B. TGFβ in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity. 2006;24:179–189. - PubMed
-
- Mangan PR, et al. Transforming growth factor-β induces development of the TH17 lineage. Nature. 2006;441:231–234. - PubMed
-
- Bettelli E, et al. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 2006;441:235–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

