Ameliorating effects of auricular electroacupuncture on rectal distention-induced gastric dysrhythmias in rats
- PMID: 25643282
- PMCID: PMC4313944
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114226
Ameliorating effects of auricular electroacupuncture on rectal distention-induced gastric dysrhythmias in rats
Abstract
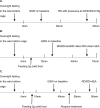
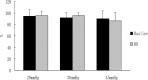
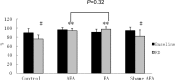
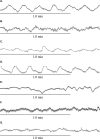
Gastric slow waves (GSW) are known to regulate gastric motility and are impaired with rectal distention (RD). Electroacupuncture (EA) at body acupoints, such as ST 36, has been shown to improve gastric dysrhythmias; however, little is known about the possible effects of auricular electroacupuncture (AEA) on GSW. To study effects and possible mechanisms of AEA on RD-induced gastric dysrhythmias in rats, ten male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats implanted with gastric serosal electrodes were studied in two different experiments in fed state. Four sessions were performed in experiment 1 as follows: control (RD, no stimulation), RD+AEA, RD+EA at body points and RD+sham AEA. Two sessions were included in experiment 2 to study mechanisms of AEA: RD + atropine and RD + atropine + AEA. It was found that 1) RD significantly decreased the percentage of normal GSW from 89.8 ± 3.5% to 76.0 ± 3.3% (P<0.05); 2) AEA increased the percentage of normal GSW during RD to 94.0 ± 2.1% (P<0.05 vs. RD) via a reduction in the percentages of tachygastria and arrhythmia (P<0.05 vs. RD); 3) atropine blocked the ameliorating effect of AEA on RD-induced gastric dysrhythmias. Our results demonstrated that RD induces gastric dysrhythmias in fed state in rats. AEA improves RD-induced gastric dysrhythmias via the vagal pathway. AEA may have a therapeutic potential in treating gastric dysrhythmias.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Wang J, Song J, Hou X, Liu J, Chen JD (2010) Effects of cutaneous gastric electrical stimulation on gastric emptying and postprandial satiety and fullness in lean and obese subjects. J Clin Gastroenterol. 44: 335–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

