Mechanisms of maladaptive repair after AKI leading to accelerated kidney ageing and CKD
- PMID: 25643664
- PMCID: PMC4412815
- DOI: 10.1038/nrneph.2015.3
Mechanisms of maladaptive repair after AKI leading to accelerated kidney ageing and CKD
Abstract
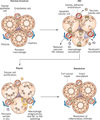
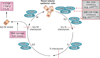
Acute kidney injury is an increasingly common complication of hospital admission and is associated with high levels of morbidity and mortality. A hypotensive, septic, or toxic insult can initiate a cascade of events, resulting in impaired microcirculation, activation of inflammatory pathways and tubular cell injury or death. These processes ultimately result in acutely impaired kidney function and initiation of a repair response. This Review explores the various mechanisms responsible for the initiation and propagation of acute kidney injury, the prototypic mechanisms by which a substantially damaged kidney can regenerate its normal architecture, and how the adaptive processes of repair can become maladaptive. These mechanisms, which include G2/M cell-cycle arrest, cell senescence, profibrogenic cytokine production, and activation of pericytes and interstitial myofibroblasts, contribute to the development of progressive fibrotic kidney disease. The end result is a state that mimics accelerated kidney ageing. These mechanisms present important opportunities for the design of targeted therapeutic strategies to promote adaptive renal recovery and minimize progressive fibrosis and chronic kidney disease after acute insults.
Figures




References
-
- Metcalfe W, et al. Acute renal failure requiring renal replacement therapy: incidence and outcome. QJM. 2002;95:579–583. - PubMed
-
- Ali T, et al. Incidence and outcomes in acute kidney injury: A comprehensive population-based study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007;18:1292–1298. - PubMed
-
- Noble JS, Simpson K, Allison ME. Long-term quality of life and hospital mortality in patients treated with intermittent or continuous hemodialysis for acute renal and respiratory failure. Ren. Fail. 2006;28:323–330. - PubMed
-
- Xue JL, et al. Incidence and mortality of acute renal failure in medicare beneficiaries, 1992 to 2001. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006;17:1135–1142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

