Binding of complement factor H to PorB3 and NspA enhances resistance of Neisseria meningitidis to anti-factor H binding protein bactericidal activity
- PMID: 25644002
- PMCID: PMC4363443
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.02984-14
Binding of complement factor H to PorB3 and NspA enhances resistance of Neisseria meningitidis to anti-factor H binding protein bactericidal activity
Abstract
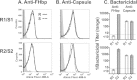
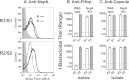
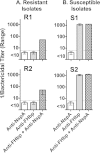
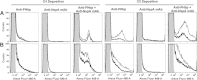
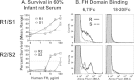
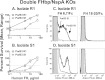
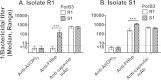
Among 25 serogroup B Neisseria meningitidis clinical isolates, we identified four (16%) with high factor H binding protein (FHbp) expression that were resistant to complement-mediated bactericidal activity of sera from mice immunized with recombinant FHbp vaccines. Two of the four isolates had evidence of human FH-dependent complement downregulation independent of FHbp. Since alternative complement pathway recruitment is critical for anti-FHbp bactericidal activity, we hypothesized that in these two isolates binding of FH to ligands other than FHbp contributes to anti-FHbp bactericidal resistance. Knocking out NspA, a known meningococcal FH ligand, converted both resistant isolates to anti-FHbp susceptible isolates. The addition of a nonbactericidal anti-NspA monoclonal antibody to the bactericidal reaction also increased anti-FHbp bactericidal activity. To identify a role for FH ligands other than NspA or FHbp in resistance, we created double NspA/FHbp knockout mutants. Mutants from both resistant isolates bound 10-fold more recombinant human FH domains 6 and 7 fused to Fc than double knockout mutants prepared from two sensitive meningococcal isolates. In light of recent studies showing functional FH-PorB2 interactions, we hypothesized that PorB3 from the resistant isolates recruited FH. Allelic exchange of porB3 from a resistant isolate to a sensitive isolate increased resistance of the sensitive isolate to anti-FHbp bactericidal activity (and vice versa). Thus, some PorB3 variants functionally bind human FH, which in the presence of NspA enhances anti-FHbp resistance. Combining anti-NspA antibodies with anti-FHbp antibodies can overcome resistance. Meningococcal vaccines that target both NspA and FHbp are likely to confer greater protection than either antigen alone.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Factor H-dependent alternative pathway inhibition mediated by porin B contributes to virulence of Neisseria meningitidis.mBio. 2013 Oct 15;4(5):e00339-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00339-13. mBio. 2013. PMID: 24129254 Free PMC article.
-
A Meningococcal Outer Membrane Vesicle Vaccine with Overexpressed Mutant FHbp Elicits Higher Protective Antibody Responses in Infant Rhesus Macaques than a Licensed Serogroup B Vaccine.mBio. 2019 Jun 18;10(3):e01231-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01231-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31213564 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of Complement Factor H (FH) Decreases Protective Anti-FH Binding Protein Antibody Responses of Infant Rhesus Macaques Immunized With a Meningococcal Serogroup B Vaccine.J Infect Dis. 2015 Sep 1;212(5):784-92. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv081. Epub 2015 Feb 12. J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25676468 Free PMC article.
-
Does binding of complement factor H to the meningococcal vaccine antigen, factor H binding protein, decrease protective serum antibody responses?Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013 Aug;20(8):1099-107. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00260-13. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23740919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meningococcal factor H binding protein as immune evasion factor and vaccine antigen.FEBS Lett. 2020 Aug;594(16):2657-2669. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13793. Epub 2020 May 12. FEBS Lett. 2020. PMID: 32298465 Review.
Cited by
-
Broad vaccine protection against Neisseria meningitidis using factor H binding protein.Vaccine. 2020 Nov 17;38(49):7716-7727. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.08.031. Epub 2020 Aug 30. Vaccine. 2020. PMID: 32878710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variation in CFHR3 determines susceptibility to meningococcal disease by controlling factor H concentrations.Am J Hum Genet. 2022 Sep 1;109(9):1680-1691. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2022.08.001. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Am J Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 36007525 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility of Meningococcal Strains Responsible for Two Serogroup B Outbreaks on U.S. University Campuses to Serum Bactericidal Activity Elicited by the MenB-4C Vaccine.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015 Dec;22(12):1227-34. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00474-15. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26424832 Free PMC article.
-
Properdin: a tightly regulated critical inflammatory modulator.Immunol Rev. 2016 Nov;274(1):172-190. doi: 10.1111/imr.12466. Immunol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27782331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low Levels of Factor H Family Proteins During Meningococcal Disease Indicate Systemic Processes Rather Than Specific Depletion by Neisseria meningitidis.Front Immunol. 2022 May 26;13:876776. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.876776. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35720329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McNeil LK, Zagursky RJ, Lin SL, Murphy E, Zlotnick GW, Hoiseth SK, Jansen KU, Anderson AS. 2013. Role of factor H binding protein in Neisseria meningitidis virulence and its potential as a vaccine candidate to broadly protect against meningococcal disease. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77:234–252. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00056-12. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fletcher LD, Bernfield L, Barniak V, Farley JE, Howell A, Knauf M, Ooi P, Smith RP, Weise P, Wetherell M, Xie X, Zagursky R, Zhang Y, Zlotnick GW. 2004. Vaccine potential of the Neisseria meningitidis 2086 lipoprotein. Infect Immun 72:2088–2100. doi:10.1128/IAI.72.4.2088-2100.2004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murphy E, Andrew L, Lee KL, Dilts DA, Nunez L, Fink PS, Ambrose K, Borrow R, Findlow J, Taha MK, Deghmane AE, Kriz P, Musilek M, Kalmusova J, Caugant DA, Alvestad T, Mayer LW, Sacchi CT, Wang X, Martin D, von Gottberg A, du Plessis M, Klugman KP, Anderson AS, Jansen KU, Zlotnick GW, Hoiseth SK. 2009. Sequence diversity of the factor H binding protein vaccine candidate in epidemiologically relevant strains of serogroup B Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis 200:379–389. doi:10.1086/600141. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Masignani V, Comanducci M, Giuliani MM, Bambini S, Adu-Bobie J, Arico B, Brunelli B, Pieri A, Santini L, Savino S, Serruto D, Litt D, Kroll S, Welsch JA, Granoff DM, Rappuoli R, Pizza M. 2003. Vaccination against Neisseria meningitidis using three variants of the lipoprotein GNA1870. J Exp Med 197:789–799. doi:10.1084/jem.20021911. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

