DAT isn't all that: cocaine reward and reinforcement require Toll-like receptor 4 signaling
- PMID: 25644383
- PMCID: PMC4523496
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2014.177
DAT isn't all that: cocaine reward and reinforcement require Toll-like receptor 4 signaling
Abstract
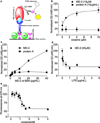
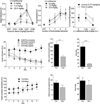
The initial reinforcing properties of drugs of abuse, such as cocaine, are largely attributed to their ability to activate the mesolimbic dopamine system. Resulting increases in extracellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) are traditionally thought to result from cocaine's ability to block dopamine transporters (DATs). Here we demonstrate that cocaine also interacts with the immunosurveillance receptor complex, Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), on microglial cells to initiate central innate immune signaling. Disruption of cocaine signaling at TLR4 suppresses cocaine-induced extracellular dopamine in the NAc, as well as cocaine conditioned place preference and cocaine self-administration. These results provide a novel understanding of the neurobiological mechanisms underlying cocaine reward/reinforcement that includes a critical role for central immune signaling, and offer a new target for medication development for cocaine abuse treatment.
Figures





References
-
- Pontieri FE, Tanda G, Di Chiara G. Intravenous cocaine, morphine, and amphetamine preferentially increase extracellular dopamine in the “shell” as compared with the “core” of the rat nucleus accumbens. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1995;92:12304–12308. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Koob GF, Bloom FE. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of drug dependence. Science. 1988;242:715–723. - PubMed
-
- Volkow ND, et al. Relationship between subjective effects of cocaine and dopamine transporter occupancy. Nature. 1997;386:827–830. - PubMed
-
- Ritz MC, Lamb RJ, Goldberg SR, Kuhar MJ. Cocaine receptors on dopamine transporters are related to self-administration of cocaine. Science. 1987;237:1219–1223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DA029420/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA017637/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- GM103843/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA026950/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM101279/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- GM101279/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA033358/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA033358/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DA029240/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM103843/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01DA-9-8883/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE021966/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA023132/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

