Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta is a functional binding partner for vascular endothelial growth factor
- PMID: 25644401
- PMCID: PMC4323219
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-015-0287-3
Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta is a functional binding partner for vascular endothelial growth factor
Abstract
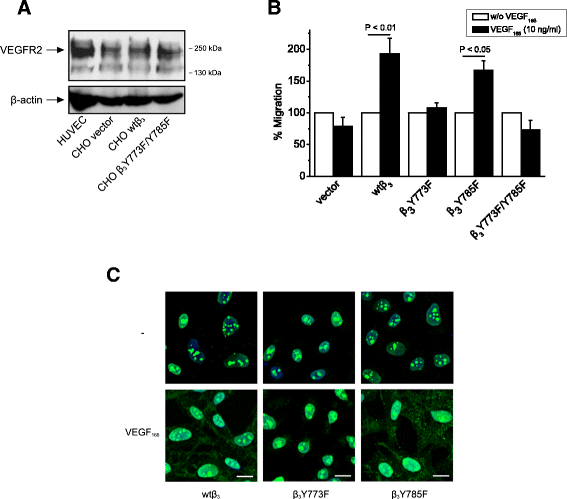
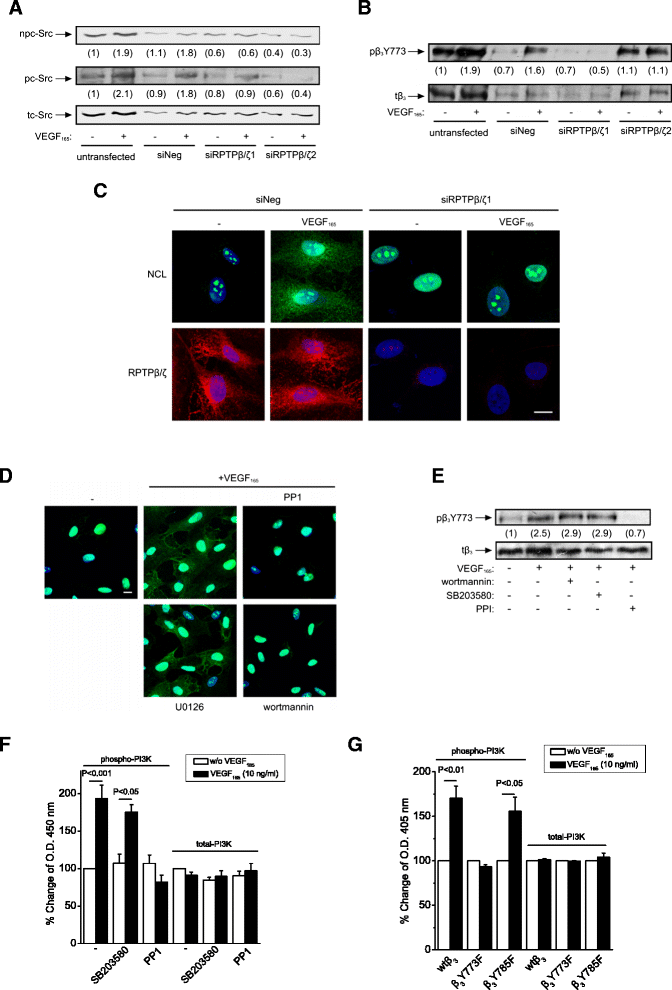
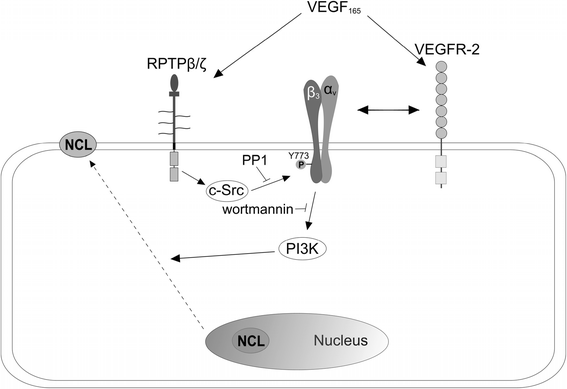
Background: Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta (RPTPβ/ζ) is a chondroitin sulphate (CS) transmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatase and is a receptor for pleiotrophin (PTN). RPTPβ/ζ interacts with ανβ₃ on the cell surface and upon binding of PTN leads to c-Src dephosphorylation at Tyr530, β₃ Tyr773 phosphorylation, cell surface nucleolin (NCL) localization and stimulation of cell migration. c-Src-mediated β₃ Tyr773 phosphorylation is also observed after vascular endothelial growth factor 165 (VEGF₁₆₅) stimulation of endothelial cells and is essential for VEGF receptor type 2 (VEGFR2) - ανβ₃ integrin association and subsequent signaling. In the present work, we studied whether RPTPβ/ζ mediates angiogenic actions of VEGF.
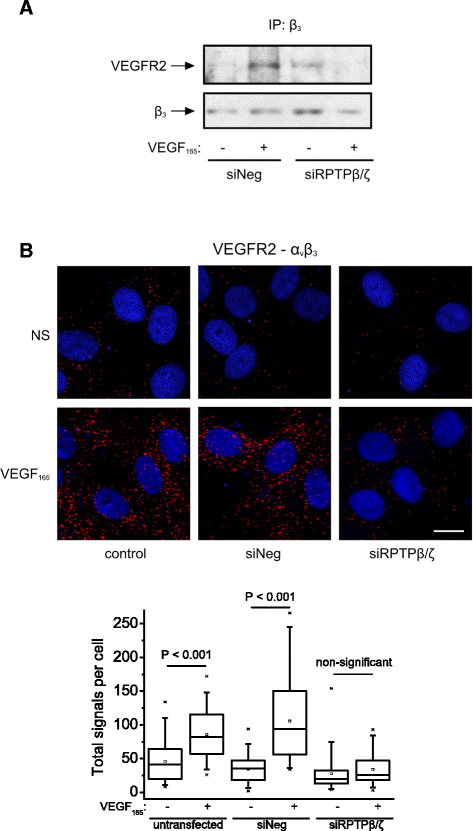
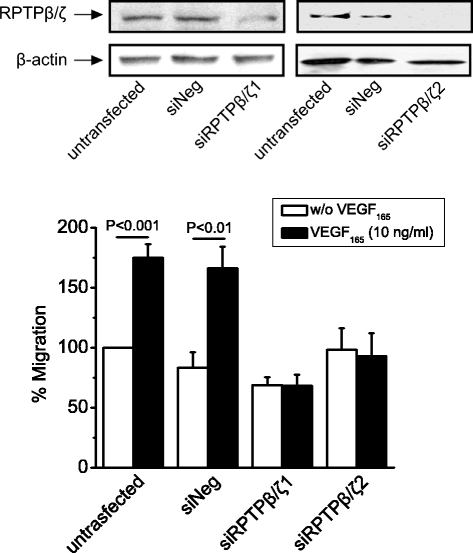
Methods: Human umbilical vein endothelial, human glioma U87MG and stably transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells expressing different β₃ subunits were used. Protein-protein interactions were studied by a combination of immunoprecipitation/Western blot, immunofluorescence and proximity ligation assays, properly quantified as needed. RPTPβ/ζ expression was down-regulated using small interference RNA technology. Migration assays were performed in 24-well microchemotaxis chambers, using uncoated polycarbonate membranes with 8 μm pores.
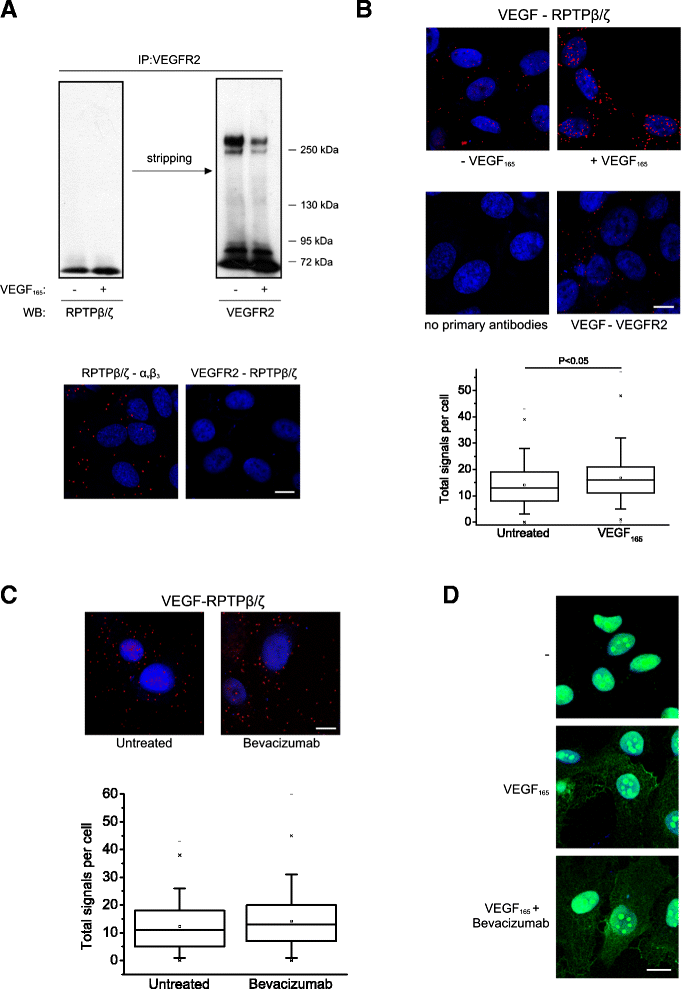
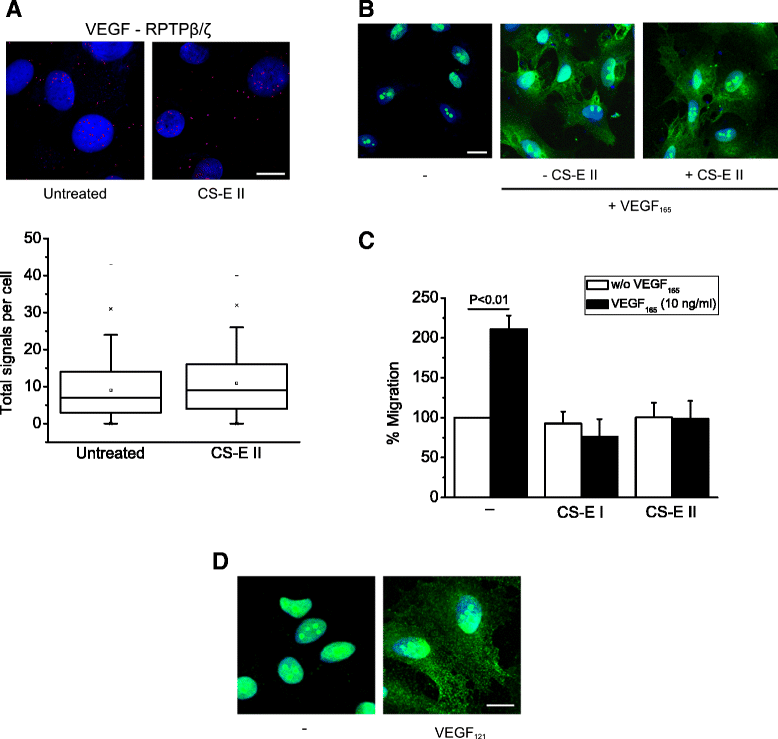
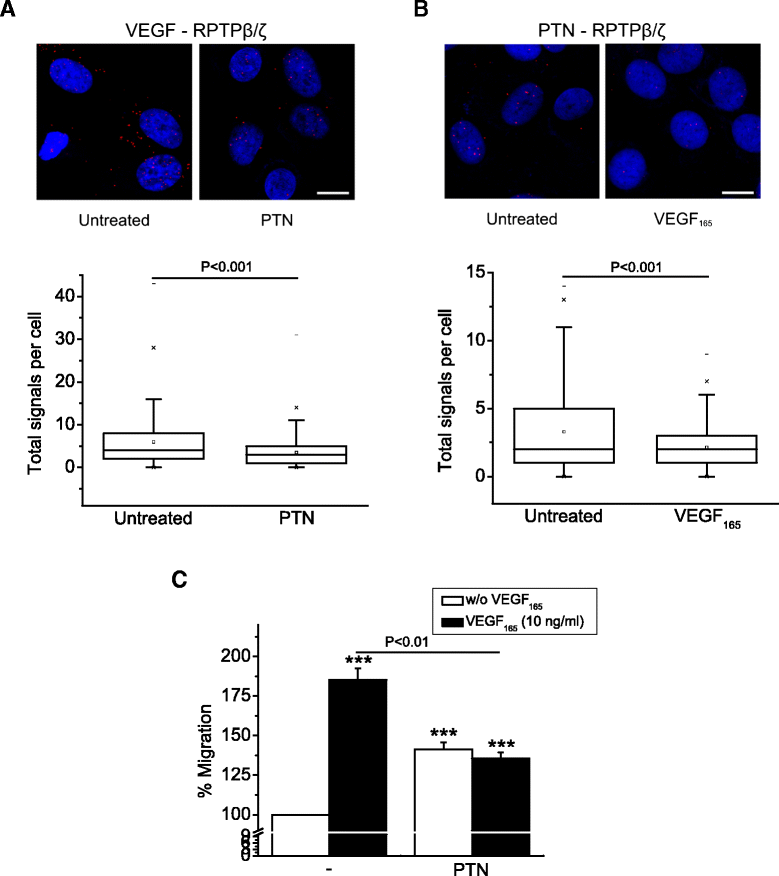
Results: RPTPβ/ζ mediates VEGF₁₆₅-induced c-Src-dependent β₃ Tyr773 phosphorylation, which is required for VEGFR2-ανβ₃ interaction and the downstream activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and cell surface NCL localization. RPTPβ/ζ directly interacts with VEGF165, and this interaction is not affected by bevacizumab, while it is interrupted by both CS-E and PTN. Down-regulation of RPTPβ/ζ by siRNA or administration of exogenous CS-E abolishes VEGF₁₆₅-induced endothelial cell migration, while PTN inhibits the migratory effect of VEGF₁₆₅ to the levels of its own effect.
Conclusions: These data identify RPTPβ/ζ as a cell membrane binding partner for VEGF that regulates angiogenic functions of endothelial cells and suggest that it warrants further validation as a potential target for development of additive or alternative anti-VEGF therapies.
Figures
References
-
- Koutsioumpa M, Papadimitriou E: PG receptors with phosphatase action in cancer and angiogenesis. In Extracellular Matrix: Pathobiology and Signalling. Edited by Karamanos N. Berlin/Boston: Walter de Gruyter GmbH and Co KG; 2012:813–823.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

