RIG-I-like receptor regulation in virus infection and immunity
- PMID: 25644461
- PMCID: PMC5076476
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2015.01.004
RIG-I-like receptor regulation in virus infection and immunity
Abstract
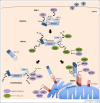
Mammalian cells have the intrinsic capacity to detect viral pathogens and to initiate an antiviral response that is characterized by the induction of interferons (IFNs) and proinflammatory cytokines. A delicate regulation of the signaling pathways that lead to cytokine production is needed to ensure effective clearance of the virus, while preventing tissue damage caused by excessive cytokine release. Here, we focus on the mechanisms that modulate the signal transduction triggered by RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) and their adaptor protein MAVS, key components of the host machinery for sensing foreign RNA. Specifically, we summarize recent advances in understanding how RLR signaling is regulated by posttranslational and posttranscriptional mechanisms, microRNAs (miRNAs) and autophagy. We further discuss how viruses target these regulatory mechanisms for immune evasion.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

