Mechanisms of Gefitinib-mediated reversal of tamoxifen resistance in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by inducing ERα re-expression
- PMID: 25644501
- PMCID: PMC4314651
- DOI: 10.1038/srep07835
Mechanisms of Gefitinib-mediated reversal of tamoxifen resistance in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by inducing ERα re-expression
Abstract
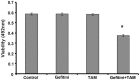
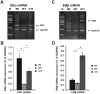
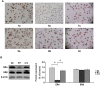
Estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer patients may turn ER-negative and develop acquired drug resistance, which compromises the efficacy of endocrine therapy. By investigating the phenomenon that gefitinib can re-sensitise tamoxifen (TAM)-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells (MCF-7/TAM) to TAM, the present study verified that gefitinib could reverse the acquired drug resistance in endocrine therapy and further explored the underlying mechanism.ERα-negative MCF-7/TAM cells were established. Upon treating the cells with gefitinib, the mRNA and protein levels of ERα and ERβ, as well as the expression of molecules involved in the MAPK pathway, were examined using the RT-PCR and immunocytochemistry. The RT-PCR results showed that the mRNA levels of ERα and ERβ in MCF-7/TAM cells were up-regulated following gefitinib treatment; specifically, ERα was re-expressed, and ERβ expression was up-regulated. The expression of molecules involved in the MAPK pathway, including RAS, MEK1/2, and p-ERK1/2, in MCF-7/TAM cells was significantly up-regulated, compared with MCF-7 cells. After the gefitinib treatment, the expression levels of MEK1/2 and p-ERK1/2 were significantly down-regulated. ERα loss is the primary cause for TAM resistance. Gefitinib reverses TAM resistance primarily by up-regulating the ERα mRNA level and inducing the re-expression of ERα. The MAPK pathway plays a key role in ERα re-expression.
Figures


References
-
- Johnston S. R. Acquired tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer-potential mechanisms and clinical implications. Anticancer Drugs 8, 911–930 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Smith R. A., Cokkinides V. & Brooks D. Cancer screening in the United States, 2011: A review of current American Cancer Society guidelines and issues in cancer screening. CA Cancer J Clin 61, 8–30 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trailist Collaborative Group. Tamoxifen for early breast cancer:an overview of the randomized trials. Lancet 351, 1451–1467 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Harvey J. M., Clark G. M., Osborne C. K. & Allred D. C. Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J ClinOncol 17, 1474–1481 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

