Chromatin signatures of cancer
- PMID: 25644600
- PMCID: PMC4318141
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.255182.114
Chromatin signatures of cancer
Abstract
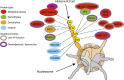
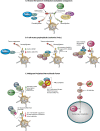
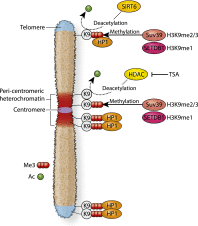
Changes in the pattern of gene expression play an important role in allowing cancer cells to acquire their hallmark characteristics, while genomic instability enables cells to acquire genetic alterations that promote oncogenesis. Chromatin plays central roles in both transcriptional regulation and the maintenance of genomic stability. Studies by cancer genome consortiums have identified frequent mutations in genes encoding chromatin regulatory factors and histone proteins in human cancer, implicating them as major mediators in the pathogenesis of both hematological malignancies and solid tumors. Here, we review recent advances in our understanding of the role of chromatin in cancer, focusing on transcriptional regulatory complexes, enhancer-associated factors, histone point mutations, and alterations in heterochromatin-interacting factors.
Keywords: cancer; chromatin; histone proteins.
© 2015 Morgan and Shilatifard; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
References
-
- Aagaard L, Laible G, Selenko P, Schmid M, Dorn R, Schotta G, Kuhfittig S, Wolf A, Lebersorger A, Singh PB, et al. 1999. Functional mammalian homologues of the Drosophila PEV-modifier Su(var)3-9 encode centromere-associated proteins which complex with the heterochromatin component M31. EMBO J 18: 1923–1938. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, Allshire RC, Kouzarides T. 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410: 120–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
