Activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal stress axis induces cellular oxidative stress
- PMID: 25646076
- PMCID: PMC4298223
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00456
Activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal stress axis induces cellular oxidative stress
Abstract
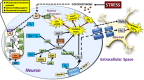
Glucocorticoids released from the adrenal gland in response to stress-induced activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis induce activity in the cellular reduction-oxidation (redox) system. The redox system is a ubiquitous chemical mechanism allowing the transfer of electrons between donor/acceptors and target molecules during oxidative phosphorylation while simultaneously maintaining the overall cellular environment in a reduced state. The objective of this review is to present an overview of the current literature discussing the link between HPA axis-derived glucocorticoids and increased oxidative stress, particularly focussing on the redox changes observed in the hippocampus following glucocorticoid exposure.
Keywords: corticosterone; hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species; redox status; stress.
Figures
References
-
- Barycki J. J., Asard H., Stone J. M., Wilson M. A., Banerjee R., Becker D. F. (2007). Antioxidant Molecules and Redox Cofactors, Redox Biochemistry. (Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc; ).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

