Genome-wide association study of clinically defined gout identifies multiple risk loci and its association with clinical subtypes
- PMID: 25646370
- PMCID: PMC4819613
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206191
Genome-wide association study of clinically defined gout identifies multiple risk loci and its association with clinical subtypes
Abstract
Objective: Gout, caused by hyperuricaemia, is a multifactorial disease. Although genome-wide association studies (GWASs) of gout have been reported, they included self-reported gout cases in which clinical information was insufficient. Therefore, the relationship between genetic variation and clinical subtypes of gout remains unclear. Here, we first performed a GWAS of clinically defined gout cases only.
Methods: A GWAS was conducted with 945 patients with clinically defined gout and 1213 controls in a Japanese male population, followed by replication study of 1048 clinically defined cases and 1334 controls.
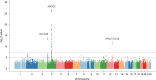
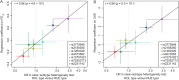
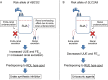
Results: Five gout susceptibility loci were identified at the genome-wide significance level (p<5.0×10(-8)), which contained well-known urate transporter genes (ABCG2 and SLC2A9) and additional genes: rs1260326 (p=1.9×10(-12); OR=1.36) of GCKR (a gene for glucose and lipid metabolism), rs2188380 (p=1.6×10(-23); OR=1.75) of MYL2-CUX2 (genes associated with cholesterol and diabetes mellitus) and rs4073582 (p=6.4×10(-9); OR=1.66) of CNIH-2 (a gene for regulation of glutamate signalling). The latter two are identified as novel gout loci. Furthermore, among the identified single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), we demonstrated that the SNPs of ABCG2 and SLC2A9 were differentially associated with types of gout and clinical parameters underlying specific subtypes (renal underexcretion type and renal overload type). The effect of the risk allele of each SNP on clinical parameters showed significant linear relationships with the ratio of the case-control ORs for two distinct types of gout (r=0.96 [p=4.8×10(-4)] for urate clearance and r=0.96 [p=5.0×10(-4)] for urinary urate excretion).
Conclusions: Our findings provide clues to better understand the pathogenesis of gout and will be useful for development of companion diagnostics.
Keywords: Arthritis; Gene Polymorphism; Gout.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures

Similar articles
-
Variants in urate transporters, ADH1B, GCKR and MEPE genes associate with transition from asymptomatic hyperuricaemia to gout: results of the first gout versus asymptomatic hyperuricaemia GWAS in Caucasians using data from the UK Biobank.Ann Rheum Dis. 2021 Sep;80(9):1220-1226. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-219796. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021. PMID: 33832965
-
Trans-ancestral dissection of urate- and gout-associated major loci SLC2A9 and ABCG2 reveals primate-specific regulatory effects.J Hum Genet. 2021 Feb;66(2):161-169. doi: 10.1038/s10038-020-0821-z. Epub 2020 Aug 10. J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 32778763
-
An update on the genetic architecture of hyperuricemia and gout.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Apr 10;17(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0609-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25889045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GWAS of clinically defined gout and subtypes identifies multiple susceptibility loci that include urate transporter genes.Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 May;76(5):869-877. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209632. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 27899376 Free PMC article.
-
The association between genetic polymorphisms in ABCG2 and SLC2A9 and urate: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med Genet. 2020 Oct 21;21(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s12881-020-01147-2. BMC Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 33087043 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of rs671, a common variant of ALDH2, as a gout susceptibility locus.Sci Rep. 2016 May 16;6:25360. doi: 10.1038/srep25360. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27181629 Free PMC article.
-
Urate Handling in the Human Body.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2016 Jun;18(6):34. doi: 10.1007/s11926-016-0587-7. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27105641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathway for ascertaining the role of uric acid in neurodegenerative diseases.Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2022 Jun 21;14(1):e12329. doi: 10.1002/dad2.12329. eCollection 2022. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2022. PMID: 35769871 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Common variant of BCAS3 is associated with gout risk in Japanese population: the first replication study after gout GWAS in Han Chinese.BMC Med Genet. 2018 Jun 7;19(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12881-018-0583-z. BMC Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 29879923 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of obesity on the association between MYL2 (rs3782889) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol among Korean men.J Hum Genet. 2016 May;61(5):405-9. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2015.165. Epub 2016 Jan 14. J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 26763873
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

