Hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 25646384
- PMCID: PMC4315912
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021444
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
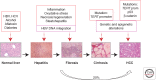
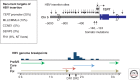
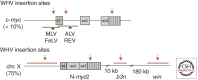
The hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a widespread human pathogen that causes liver inflammation, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent sequencing technologies have refined our knowledge of the genomic landscape and pathogenesis of HCC, but the mechanisms by which HBV exerts its oncogenic role remain controversial. In a prevailing view, inflammation, liver damage, and regeneration may foster the accumulation of genetic and epigenetic defects leading to cancer onset. However, a more direct and specific contribution of the virus is supported by clinical and biological observations. Among genetically heterogeneous HCCs, HBV-related tumors display high genomic instability, which may be attributed to the ability of HBV to integrate its DNA into the host cell genome, provoking chromosomal alterations and insertional mutagenesis of cancer genes. The viral transactivator HBx may also participate in transformation by deregulating diverse cellular machineries. A better understanding of the complex mechanisms linking HBV to HCC will improve prevention and treatment strategies.
Copyright © 2015 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Beasley RP, Lin CC, Hwang LY, Chien CS 1981. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus: A prospective study of 22,707 men in Taiwan. Lancet 2: 1129–1133. - PubMed
-
- Benhenda S, Cougot D, Buendia MA, Neuveut C 2009. Hepatitis B virus X protein molecular functions and its role in virus life cycle and pathogenesis. Adv Cancer Res 103: 75–109. - PubMed
-
- Boyault S, Rickman DS, de Reynies A, Balabaud C, Rebouissou S, Jeannot E, Herault A, Saric J, Belghiti J, Franco D, et al. 2007. Transcriptome classification of HCC is related to gene alterations and to new therapeutic targets. Hepatology 45: 42–52. - PubMed
-
- Bréchot C, Pourcel C, Louise A, Rain B, Tiollais P 1980. Presence of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA sequences in cellular DNA of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature 286: 533–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
