Suppression of EEG visual-evoked potentials in rats through neuromodulatory focused ultrasound
- PMID: 25646585
- PMCID: PMC4326564
- DOI: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000330
Suppression of EEG visual-evoked potentials in rats through neuromodulatory focused ultrasound
Abstract
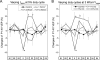
We investigated the use of pulsed low-intensity focused ultrasound (FUS) to suppress the visual neural response induced by light stimulation in rodents. FUS was administered transcranially to the rat visual cortex using different acoustic intensities and pulsing duty cycles. The visual-evoked potentials (VEPs) generated by an external strobe light stimulation were measured three times before, once during, and five times after the sonication. The VEP magnitude was suppressed during the sonication using a 5% duty cycle (pulse-repetition frequency of 100 Hz) and a spatial-peak pulse-average acoustic intensity of 3 W/cm; however, this suppressive effect was not present when a lower acoustic intensity and duty cycle were used. The application of a higher intensity and duty cycle resulted in a slight elevation in VEP magnitude, which suggested excitatory neuromodulation. Our findings demonstrate that the application of pulsed FUS to the region-specific brain area not only suppresses its excitability, but can also enhance the excitability depending on the acoustic intensity and the rate of energy deposition. This bimodal feature of FUS-mediated neuromodulation, which has been predicted by numerical models on neural membrane capacitance change by the external acoustic pressure waves, suggests its versatility for neurotherapeutic applications.
Figures
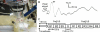
References
-
- Hoy KE, Fitzgerald PB. Brain stimulation in psychiatry and its effects on cognition. Nature reviews Neurology. 2010;6:267–275. - PubMed
-
- Miller KJ, denNijs M, Shenoy P, Miller JW, Rao RPN, Ojemann JG. Real-time functional brain mapping using electrocorticography. Neuroimage. 2007;37:504–507. - PubMed
-
- Fregni F, Pascual-Leone A. Technology insight: noninvasive brain stimulation in neurology-perspectives on the therapeutic potential of rTMS and tDCS. Nature clinical practice Neurology. 2007;3:383–393. - PubMed
-
- Bystritsky A, Korb AS, Douglas PK, Cohen MS, Melega WP, Mulgaonkar AP, et al. A review of low-intensity focused ultrasound pulsation. Brain Stimul. 2011;4:125–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

