Prenylation inhibition-induced cell death in melanoma: reduced sensitivity in BRAF mutant/PTEN wild-type melanoma cells
- PMID: 25646931
- PMCID: PMC4315579
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117021
Prenylation inhibition-induced cell death in melanoma: reduced sensitivity in BRAF mutant/PTEN wild-type melanoma cells
Abstract
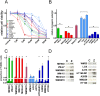
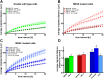
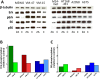
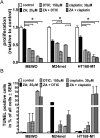
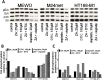
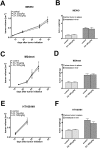
While targeted therapy brought a new era in the treatment of BRAF mutant melanoma, therapeutic options for non-BRAF mutant cases are still limited. In order to explore the antitumor activity of prenylation inhibition we investigated the response to zoledronic acid treatment in thirteen human melanoma cell lines with known BRAF, NRAS and PTEN mutational status. Effect of zoledronic acid on proliferation, clonogenic potential, apoptosis and migration of melanoma cells as well as the activation of downstream elements of the RAS/RAF pathway were investigated in vitro with SRB, TUNEL and PARP cleavage assays and videomicroscopy and immunoblot measurements, respectively. Subcutaneous and spleen-to-liver colonization xenograft mouse models were used to evaluate the influence of zoledronic acid treatment on primary and disseminated tumor growth of melanoma cells in vivo. Zoledronic acid more efficiently decreased short-term in vitro viability in NRAS mutant cells when compared to BRAF mutant and BRAF/NRAS wild-type cells. In line with this finding, following treatment decreased activation of ribosomal protein S6 was found in NRAS mutant cells. Zoledronic acid demonstrated no significant synergism in cell viability inhibition or apoptosis induction with cisplatin or DTIC treatment in vitro. Importantly, zoledronic acid could inhibit clonogenic growth in the majority of melanoma cell lines except in the three BRAF mutant but PTEN wild-type melanoma lines. A similar pattern was observed in apoptosis induction experiments. In vivo zoledronic acid did not inhibit the subcutaneous growth or spleen-to-liver colonization of melanoma cells. Altogether our data demonstrates that prenylation inhibition may be a novel therapeutic approach in NRAS mutant melanoma. Nevertheless, we also demonstrated that therapeutic sensitivity might be influenced by the PTEN status of BRAF mutant melanoma cells. However, further investigations are needed to identify drugs that have appropriate pharmacological properties to efficiently target prenylation in melanoma cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sensitivity of Melanoma Cells to EGFR and FGFR Activation but Not Inhibition is Influenced by Oncogenic BRAF and NRAS Mutations.Pathol Oncol Res. 2015 Sep;21(4):957-68. doi: 10.1007/s12253-015-9916-9. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Pathol Oncol Res. 2015. PMID: 25749811
-
KIT, NRAS, BRAF and PTEN mutations in a sample of Swedish patients with acral lentiginous melanoma.J Dermatol Sci. 2013 Dec;72(3):284-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.07.013. Epub 2013 Aug 8. J Dermatol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23993026
-
Inhibition of MERTK Promotes Suppression of Tumor Growth in BRAF Mutant and BRAF Wild-Type Melanoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2019 Feb;18(2):278-288. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0456. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 30482852 Free PMC article.
-
[vestigation of molecular factors determining BRAF-inhibitor sensitivity in solid tumors].Magy Onkol. 2020 Mar 17;64(1):76-78. Epub 2019 Oct 27. Magy Onkol. 2020. PMID: 32181767 Review. Hungarian.
-
The role of MEK inhibitors in the treatment of metastatic melanoma.Curr Opin Oncol. 2014 Mar;26(2):196-203. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000050. Curr Opin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24419498 Review.
Cited by
-
Bisphosphonates: The role of chemistry in understanding their biological actions and structure-activity relationships, and new directions for their therapeutic use.Bone. 2022 Mar;156:116289. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2021.116289. Epub 2021 Dec 8. Bone. 2022. PMID: 34896359 Free PMC article.
-
HSPB8 counteracts tumor activity of BRAF- and NRAS-mutant melanoma cells by modulation of RAS-prenylation and autophagy.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Nov 18;13(11):973. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05365-9. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36400750 Free PMC article.
-
The Antitumor Effect of Lipophilic Bisphosphonate BPH1222 in Melanoma Models: The Role of the PI3K/Akt Pathway and the Small G Protein Rheb.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 3;20(19):4917. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194917. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31623406 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-RAF and MEK vertical inhibition enhances therapeutic response in non-V600 BRAF mutant cells.BMC Cancer. 2018 May 8;18(1):542. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4455-x. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29739364 Free PMC article.
-
K-Ras prenylation as a potential anticancer target.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020 Dec;39(4):1127-1141. doi: 10.1007/s10555-020-09902-w. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020. PMID: 32524209 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Soengas MS, Lowe SW (2003) Apoptosis and melanoma chemoresistance. Oncogene 22: 3138–3151. - PubMed
-
- Balch CM, Soong SJ, Gershenwald JE, Thompson JF, Reintgen DS, et al. (2001) Prognostic factors analysis of 17,600 melanoma patients: validation of the American Joint Committee on Cancer melanoma staging system. J Clin Oncol 19: 3622–3634. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

