Heart failure and atrial fibrillation: from basic science to clinical practice
- PMID: 25647414
- PMCID: PMC4346884
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms16023133
Heart failure and atrial fibrillation: from basic science to clinical practice
Abstract
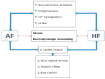
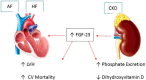
Heart failure (HF) and atrial fibrillation (AF) are two growing epidemics associated with significant morbidity and mortality. They often coexist due to common risk factors and shared pathophysiological mechanisms. Patients presenting with both HF and AF have a worse prognosis and present a particular therapeutic challenge to clinicians. This review aims to appraise the common pathophysiological background, as well as the prognostic and therapeutic implications of coexistent HF and AF.
Figures
References
-
- McMurray J.J., Adamopoulos S., Anker S.D., Auricchio A., Bohm M., Dickstein K., Falk V., Filippatos G., Fonseca C., Gomez-Sanchez M.A., et al. ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012 of the european society of cardiology: Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2012;14:803–869. doi: 10.1093/eurjhf/hfs033. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Go A.S., Hylek E.M., Phillips K.A., Chang Y., Henault L.E., Selby J.V., Singer D.E. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: National implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: The anticoagulation and risk factors in atrial fibrillation (ATRIA) study. JAMA. 2001;285:2370–2375. doi: 10.1001/jama.285.18.2370. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang T.J., Larson M.G., Levy D., Vasan R.S., Leip E.P., Wolf P.A., D’Agostino R.B., Murabito J.M., Kannel W.B., Benjamin E.J. Temporal relations of atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure and their joint influence on mortality: The framingham heart study. Circulation. 2003;107:2920–2925. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000072767.89944.6E. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

