An efficient strategy for heterologous expression and purification of active peptide hainantoxin-IV
- PMID: 25647561
- PMCID: PMC4315428
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117099
An efficient strategy for heterologous expression and purification of active peptide hainantoxin-IV
Abstract
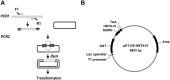
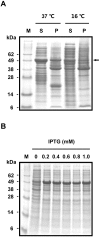
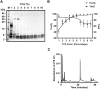
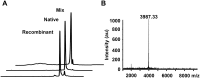
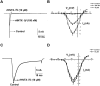
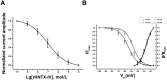
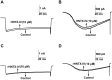
Hainantoxin-IV (HNTX-IV) from the venom of the spider Selenocosmia hainana is a potent antagonist that specifically inhibits the tetrodotoxin-sensitive (TTX-S) sodium channels. The toxin peptide consists of 35 amino acids and adopts a typical inhibitory cystine knot (ICK) motif. To obtain adequate HNTX-IV peptides for further insight into the structure-activity relationships of the toxin, a novel strategy including cloning, expression and purification was developed in an E. coli expression system. For this purpose, a seamless restriction-free (RF) cloning method was employed for the construction of an expression vector to avoid introducing unwanted sequences into the target gene. Furthermore, the solubility of recombinant HNTX-IV could be promoted efficiently by the combination of a glutathione S-transferase (GST) tag and a small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) tag. Finally, an affinity-chromatography-free purification strategy was developed by cut-off dialysis tubing combined with trichloroacetic acid (TCA) extraction. Further HPLC purification yielded recombinant, tag-free HNTX-IV with high yield and purity. The molecular weight of recombinant HNTX-IV (rHNTX-IV) is identical to its theoretical value according to Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption / Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) analysis. The recombinant toxin has similar activity (IC50 value of 120 nM) on the tetrodotoxin-sensitive (TTX-S) sodium channels in adult rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons to native toxins. In the report, an efficient and cost-effective strategy for producing rHNTX-IV was developed, which paved the way for the further study of structure-activity relationships of rHNTX-IV and its pharmaceutical applications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
A positively charged surface patch is important for hainantoxin-IV binding to voltage-gated sodium channels.J Pept Sci. 2012 Oct;18(10):643-9. doi: 10.1002/psc.2451. Epub 2012 Aug 27. J Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 22927181
-
Purification and characterization of Hainantoxin-V, a tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channel inhibitor from the venom of the spider Selenocosmia hainana.Toxicon. 2003 May;41(6):643-50. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(02)00280-5. Toxicon. 2003. PMID: 12727268
-
Heterologous expression and purification of neurotoxic Hainantoxin-III in E. coli.Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2017 Feb 7;47(2):158-162. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2016.1188313. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27249514
-
An overview of peptide toxins from the venom of the Chinese bird spider Selenocosmia huwena Wang [=Ornithoctonus huwena (Wang)].Toxicon. 2004 Apr;43(5):575-85. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2004.02.005. Toxicon. 2004. PMID: 15066414 Review.
-
Tarantulas: eight-legged pharmacists and combinatorial chemists.Toxicon. 2004 Apr;43(5):555-74. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2004.02.007. Toxicon. 2004. PMID: 15066413 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective Closed-State Nav1.7 Blocker JZTX-34 Exhibits Analgesic Effects against Pain.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Feb 2;10(2):64. doi: 10.3390/toxins10020064. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29393892 Free PMC article.
-
Current Technologies in Snake Venom Analysis and Applications.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Oct 25;16(11):458. doi: 10.3390/toxins16110458. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39591213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for Optimizing the Production of Proteins and Peptides with Multiple Disulfide Bonds.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Aug 26;9(9):541. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9090541. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32858882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bicistronic Vector Expression of Recombinant Jararhagin-C and Its Effects on Endothelial Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Dec 3;16(12):524. doi: 10.3390/toxins16120524. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39728782 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous Expression of an Insecticidal Peptide Obtained from the Transcriptome of the Colombian Spider Phoneutria depilate.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jul 2;15(7):436. doi: 10.3390/toxins15070436. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37505705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liang S, Peng X, Huang R, Chen P (1998) Biochemical identification of Selenocosmia hainana sp. nov. from south China (Araneae, Theraphosidae). Life science research/Hunan Normal University 3: 299–303.
-
- Li D, Xiao Y, Xu X, Xiong X, Lu S, et al. (2004) Structure-activity relationships of hainantoxin-IV and structure determination of active and inactive sodium channel blockers. J Biol Chem 279: 37734–37740. - PubMed
-
- Rabhi-Essafi I, Sadok A, Khalaf N, Fathallah DM (2007) A strategy for high-level expression of soluble and functional human interferon α as a GST-fusion protein in E. coli. Protein Eng Des Sel 20: 201–209. - PubMed
-
- Cain CC, Saslowsky DE, Walker RA, Shirley BW (1997) Expression of chalcone synthase and chalcone isomerase proteins in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Mol Biol 35: 377–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

