Targeting carbonic anhydrase IX activity and expression
- PMID: 25647573
- PMCID: PMC6272707
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules20022323
Targeting carbonic anhydrase IX activity and expression
Abstract
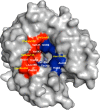
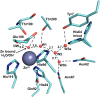
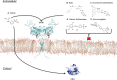
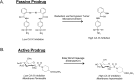
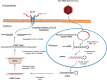
Metastatic tumors are often hypoxic exhibiting a decrease in extracellular pH (~6.5) due to a metabolic transition described by the Warburg Effect. This shift in tumor cell metabolism alters the tumor milieu inducing tumor cell proliferation, angiogenesis, cell motility, invasiveness, and often resistance to common anti-cancer treatments; hence hindering treatment of aggressive cancers. As a result, tumors exhibiting this phenotype are directly associated with poor prognosis and decreased survival rates in cancer patients. A key component to this tumor microenvironment is carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX). Knockdown of CA IX expression or inhibition of its activity has been shown to reduce primary tumor growth, tumor proliferation, and also decrease tumor resistance to conventional anti-cancer therapies. As such several approaches have been taken to target CA IX in tumors via small-molecule, anti-body, and RNAi delivery systems. Here we will review recent developments that have exploited these approaches and provide our thoughts for future directions of CA IX targeting for the treatment of cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
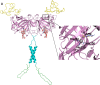


References
-
- Moulder J.E., Rockwell S. Tumor hypoxia: Its impact on cancer therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1987;5:313–341. - PubMed
-
- Wykoff C.C., Beasley N.J., Watson P.H., Turner K.J., Pastorek J., Sibtain A., Wilson G.D., Turley H., Talks K.L., Maxwell P.H., et al. Hypoxia-inducible expression of tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases. Cancer Res. 2000;60:7075–7083. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

