Genetic variants in the apoptosis gene BCL2L1 improve response to interferon-based treatment of hepatitis C virus genotype 3 infection
- PMID: 25648321
- PMCID: PMC4346890
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms16023213
Genetic variants in the apoptosis gene BCL2L1 improve response to interferon-based treatment of hepatitis C virus genotype 3 infection
Abstract
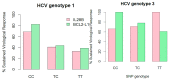
Genetic variation upstream of the apoptosis pathway has been associated with outcome of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. We investigated genetic polymorphisms in the intrinsic apoptosis pathway to assess their influence on sustained virological response (SVR) to pegylated interferon-α and ribavirin (pegIFN/RBV) treatment of HCV genotypes 1 and 3 infections. We conducted a candidate gene association study in a prospective cohort of 201 chronic HCV-infected individuals undergoing treatment with pegIFN/RBV. Differences between groups were compared in logistic regression adjusted for age, HCV viral load and interleukin 28B genotypes. Four single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) located in the B-cell lymphoma 2-like 1 (BCL2L1) gene were significantly associated with SVR. SVR rates were significantly higher for carriers of the beneficial rs1484994 CC genotypes. In multivariate logistic regression, the rs1484994 SNP combined CC+TC genotypes were associated with a 3.4 higher odds ratio (OR) in SVR for the HCV genotype 3 (p=0.02). The effect estimate was similar for genotype 1, but the association did not reach statistical significance. In conclusion, anti-apoptotic SNPs in the BCL2L1 gene were predictive of SVR to pegIFN/RBV treatment in HCV genotypes 1 and 3 infected individuals. These SNPs may be used in prediction of SVR, but further studies are needed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SNPs in the promoter region of the osteopontin gene as a marker predicting the efficacy of interferon-based therapies in patients with chronic hepatitis C.J Gastroenterol. 2005 Apr;40(4):381-8. doi: 10.1007/s00535-005-1558-3. J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15868370
-
Predictive factors of virological non-response to interferon-ribavirin combination therapy for patients infected with hepatitis C virus of genotype 1b and high viral load.J Med Virol. 2006 Jan;78(1):83-90. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20507. J Med Virol. 2006. PMID: 16299715
-
IL28B polymorphism may guide pegylated interferon plus ribavirin therapy even after curative treatment for hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.J Viral Hepat. 2011 Oct;18(10):e550-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01468.x. Epub 2011 May 23. J Viral Hepat. 2011. PMID: 21914076
-
Hepatitis C Virus and Interferon-Free Antiviral Therapeutics Revolution: Implications for Pakistan.Viral Immunol. 2017 May;30(4):252-257. doi: 10.1089/vim.2016.0164. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Viral Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28118096 Review.
-
Treatment of non-genotype 1 hepatitis C virus patients.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2012 Feb;14(1):87-93. doi: 10.1007/s11894-011-0235-3. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22113745 Review.
References
-
- TaqMan® SNP Genotyping Assays. [(accessed on 6 December 2014)]. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/SNP.
-
- Chattopadhyay K., Ramagopal U.A., Mukhopadhaya A., Malashkevich V.N., Dilorenzo T.P., Brenowitz M., Nathenson S.G., Almo S.C. Assembly and structural properties of glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor ligand: Implications for function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:19452–19457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709264104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials