Tn5/7-lux: a versatile tool for the identification and capture of promoters in gram-negative bacteria
- PMID: 25648327
- PMCID: PMC4328036
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-015-0354-3
Tn5/7-lux: a versatile tool for the identification and capture of promoters in gram-negative bacteria
Abstract
Background: The combination of imaging technologies and luciferase-based bioluminescent bacterial reporter strains provide a sensitive and simple non-invasive detection method (photonic bioimaging) for the study of diverse biological processes, as well as efficacy of therapeutic interventions, in live animal models of disease. The engineering of bioluminescent bacteria required for photonic bioimaging is frequently hampered by lack of promoters suitable for strong, yet stable luciferase gene expression.
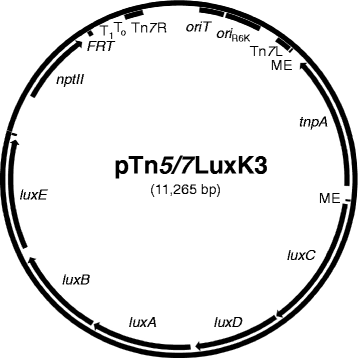
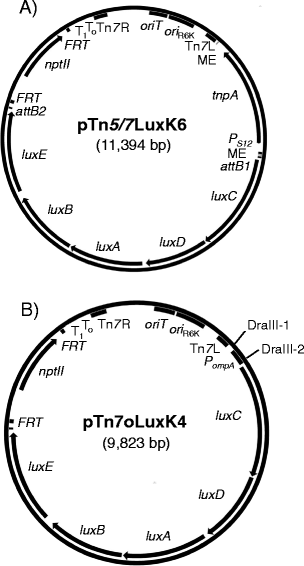
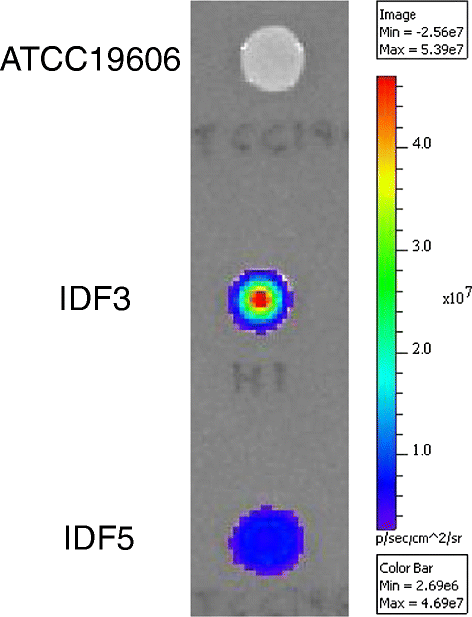
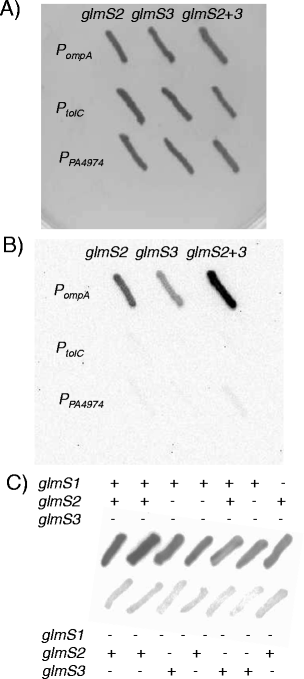
Results: We devised a novel method for identification of constitutive native promoters in Gram-negative bacteria. The method is based on a Tn5/7 transposon that exploits the unique features of Tn5 (random transposition) and Tn7 (site-specific transposition). The transposons are designed such that Tn5 transposition will allow insertion of a promoter-less bacterial luxCDABE operon downstream of a bacterial gene promoter. Cloning of DNA fragments from luminescent isolates results in a plasmid that replicates in pir (+) hosts. Sequencing of the lux-chromosomal DNA junctions on the plasmid reveals transposon insertion sites within genes or operons. The plasmid is also a mini-Tn7-lux delivery vector that can be used to introduce the promoter-lux operon fusion into other derivatives of the bacterium of interest in an isogenic fashion. Alternatively, promoter-containing sequences can be PCR-amplified from plasmid or chromosomal DNA and cloned into a series of accompanying mini-Tn7-lux vectors. The mini-Tn5/7-lux and mini-Tn7-lux vectors are equipped with diverse selection markers and thus applicable in numerous Gram-negative bacteria. Various mini-Tn5/7-lux vectors were successfully tested for transposition and promoter identification by imaging in Acinetobacter baumannii, Escherichia coli, and Burkholderia pseudomallei. Strong promoters were captured for lux expression in E. coli and A. baumannii. Some mini-Tn7-lux vectors are also equipped with attB sites for swapping of the lux operon with other reporter genes using Gateway technology.
Conclusions: Although mini-Tn5-lux and mini-Tn7-lux elements have previously been developed and used for bacterial promoter identification and chromosomal insertion of promoter-lux gene fusions, respectively, the newly developed mini-Tn5/7-lux and accompanying accessory plasmids streamline and accelerate the promoter discovery and bioluminescent strain engineering processes. Availability of vectors with diverse selection markers greatly extend the host-range of promoter probe and lux gene fusion vectors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An improved Tn7-lux reporter for broad host range, chromosomally-integrated promoter fusions in Gram-negative bacteria.J Microbiol Methods. 2015 Nov;118:75-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2015.08.016. Epub 2015 Sep 1. J Microbiol Methods. 2015. PMID: 26341612 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a Tn7-lux system for gene expression studies in gram-negative bacteria.Gene. 1992 Dec 1;122(1):27-34. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90028-n. Gene. 1992. PMID: 1333438
-
A panel of Tn7-based vectors for insertion of the gfp marker gene or for delivery of cloned DNA into Gram-negative bacteria at a neutral chromosomal site.J Microbiol Methods. 2001 Jul;45(3):187-95. doi: 10.1016/s0167-7012(01)00246-9. J Microbiol Methods. 2001. PMID: 11348676
-
Genetic tools for pseudomonads, rhizobia, and other gram-negative bacteria.Biotechniques. 2002 Feb;32(2):386-8, 390, 392-4, passim. doi: 10.2144/02322rv02. Biotechniques. 2002. PMID: 11848415 Review.
-
Applications of transposon-based gene delivery system in bacteria.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009 Mar;19(3):217-28. doi: 10.4014/jmb.0811.669. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19349746 Review.
Cited by
-
A quantitative method to assess bacterial adhesion using recombinant bioluminescent Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Biophys Rep. 2021 Feb 28;7(1):55-70. doi: 10.52601/bpr.2021.200043. Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 37288086 Free PMC article.
-
E. coli Nissle 1917-Derived Minicells for Targeted Delivery of Chemotherapeutic Drug to Hypoxic Regions for Cancer Therapy.Theranostics. 2018 Feb 12;8(6):1690-1705. doi: 10.7150/thno.21575. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29556350 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal immunization with a Bucl8-based vaccine ameliorates bacterial burden and pathological inflammation, and promotes an IgG2a/b dominant response in an outbred mouse model of Burkholderia infection.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 20;14:1177650. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1177650. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37545515 Free PMC article.
-
Versatile nourseothricin and streptomycin/spectinomycin resistance gene cassettes and their use in chromosome integration vectors.J Microbiol Methods. 2016 Oct;129:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2016.07.018. Epub 2016 Jul 22. J Microbiol Methods. 2016. PMID: 27457407 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Resistance to Folate Pathway Inhibitors in Burkholderia pseudomallei: Deviation from the Norm.mBio. 2017 Sep 5;8(5):e01357-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01357-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28874476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kadurugamuwa JL, Francis KP. Bioluminescent imaging of bacterial biofilm infections in vivo. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;431:225–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

