T cell-NF-κB activation is required for tumor control in vivo
- PMID: 25648675
- PMCID: PMC4308877
- DOI: 10.1186/s40425-014-0045-x
T cell-NF-κB activation is required for tumor control in vivo
Abstract
Background: T cells have the capacity to eliminate tumors but the signaling pathways by which they do so are incompletely understood. T cell priming requires activation of the transcription factors AP-1, NFAT and NF-κB downstream of the TCR, but whether activation of T cell-NF-κB in vivo is required for tumor control has not been addressed. In humans and mice with progressively growing tumors, the activity of T cell-intrinsic NF-κB is often reduced. However, it is not clear if this is causal for an inability to reject transformed cells, or if it is a consequence of tumor growth. T cell-NF-κB is important for T cell survival and effector differentiation and plays an important role in enabling T cells to reject cardiac and islet allografts, suggesting the possibility that it may also be required for tumor elimination. In this study, we tested whether normal T cell-NF-κB activation is necessary for the rejection of tumors whose growth is normally controlled by the immune system.
Methods: Mice with genetically impaired T cell-NF-κB activity were subcutaneously injected with MC57-SIY tumor cells. Tumor growth was measured over time, and the anti-tumor immune response was evaluated using flow cytometry and cytokine detection assays.
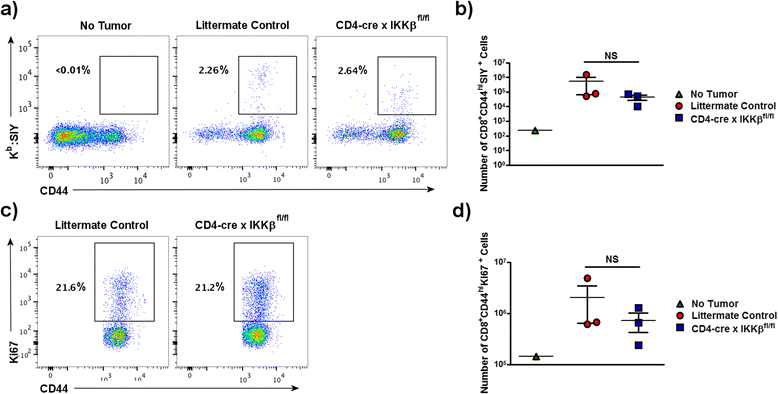
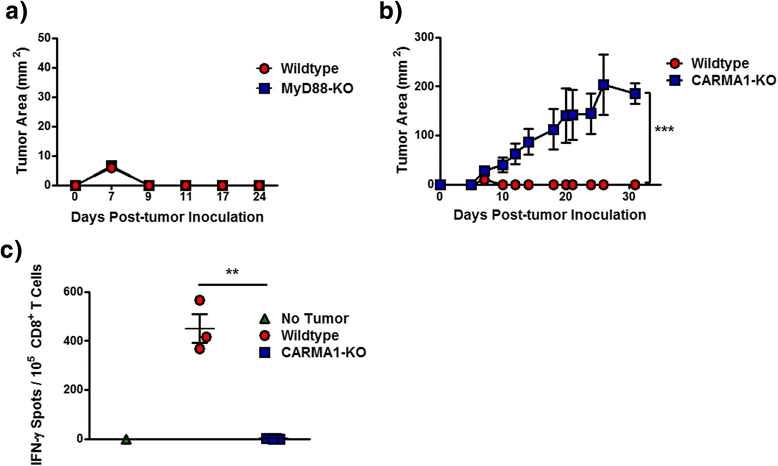
Results: Mice with impaired T cell-NF-κB activity were unable to reject tumors that were otherwise eliminated by wildtype mice, despite equal accumulation of tumor-reactive T cells. In addition, specific impairment of NF-κB signaling downstream of the TCR was sufficient to prevent tumor rejection. Tumor antigen-specific T cell-IFN-γ and TNF-α production, as well as cytotoxic ability, were all reduced in mice with impaired T cell-NF-κB, suggesting an important role for this transcription factor in the effector differentiation of tumor-specific effector T cells.
Conclusions: Our results have identified the NF-κB pathway as an important signaling axis in T cells, required for the elimination of growing tumors in vivo. Maintaining or enhancing T cell-NF-κB activity may be a promising avenue for anti-tumor immunotherapy.
Keywords: Cytokine production; Cytotoxicity; Effector function; NF-κB; Priming; T cell; Tumor rejection.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
