Preliminary efficacy of adapted responsive teaching for infants at risk of autism spectrum disorder in a community sample
- PMID: 25648749
- PMCID: PMC4306223
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/386951
Preliminary efficacy of adapted responsive teaching for infants at risk of autism spectrum disorder in a community sample
Abstract
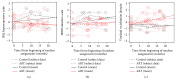
This study examined the (a) feasibility of enrolling 12-month-olds at risk of ASD from a community sample into a randomized controlled trial, (b) subsequent utilization of community services, and (c) potential of a novel parent-mediated intervention to improve outcomes. The First Year Inventory was used to screen and recruit 12-month-old infants at risk of ASD to compare the effects of 6-9 months of Adapted Responsive Teaching (ART) versus referral to early intervention and monitoring (REIM). Eighteen families were followed for ~20 months. Assessments were conducted before randomization, after treatment, and at 6-month follow-up. Utilization of community services was highest for the REIM group. ART significantly outperformed REIM on parent-reported and observed measures of child receptive language with good linear model fit. Multiphase growth models had better fit for more variables, showing the greatest effects in the active treatment phase, where ART outperformed REIM on parental interactive style (less directive), child sensory responsiveness (less hyporesponsive), and adaptive behavior (increased communication and socialization). This study demonstrates the promise of a parent-mediated intervention for improving developmental outcomes for infants at risk of ASD in a community sample and highlights the utility of earlier identification for access to community services earlier than standard practice.
Figures


References
-
- Centers for Disease Control. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years—autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2010. Surveillance Summaries. 2014;63(2):1–21. - PubMed
-
- Office of Special Education Programs. Summary Table of States' and Territories' Definitions of/Criteria for IDEA Part C Eligibility. 2004.
-
- Ringwalt S. Summary Table of States' and Territories' Definitions of/Criteria for IDEA Part C Eligibility. 2012. http://ectacenter.org/~pdfs/topics/earlyid/partc_elig_table.pdf.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

