Human islet preparations distributed for research exhibit a variety of insulin-secretory profiles
- PMID: 25648831
- PMCID: PMC4385877
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00437.2014
Human islet preparations distributed for research exhibit a variety of insulin-secretory profiles
Abstract
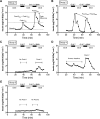
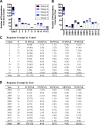
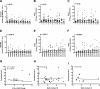
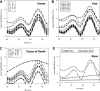
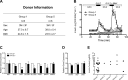
Human islet research is providing new insights into human islet biology and diabetes, using islets isolated at multiple US centers from donors with varying characteristics. This creates challenges for understanding, interpreting, and integrating research findings from the many laboratories that use these islets. In what is, to our knowledge, the first standardized assessment of human islet preparations from multiple isolation centers, we measured insulin secretion from 202 preparations isolated at 15 centers over 11 years and noted five distinct patterns of insulin secretion. Approximately three quarters were appropriately responsive to stimuli, but one quarter were dysfunctional, with unstable basal insulin secretion and/or an impairment in stimulated insulin secretion. Importantly, the patterns of insulin secretion by responsive human islet preparations (stable Baseline and Fold stimulation of insulin secretion) isolated at different centers were similar and improved slightly over the years studied. When all preparations studied were considered, basal and stimulated insulin secretion did not correlate with isolation center, biological differences of the islet donor, or differences in isolation, such as Cold Ischemia Time. Dysfunctional islet preparations could not be predicted from the information provided by the isolation center and had altered expression of genes encoding components of the glucose-sensing pathway, but not of insulin production or cell death. These results indicate that insulin secretion by most preparations from multiple centers is similar but that in vitro responsiveness of human islets cannot be predicted, necessitating preexperimental human islet assessment. These results should be considered when one is designing, interpreting, and integrating experiments using human islets.
Keywords: function; human; islet.
Figures

References
-
- Andrali SS, Virostko J, Henske J, Vanderford NL, Vinet L, Özcan S, Lamprianou S, Dai C, Radhika A, Baldwin RM, Ansari MS, Hefti F, Skovronsky D, Kung HF, Herrera PL, Peterson TE, Meda P, Powers AC. Multimodal image coregistration and inducible selective cell ablation to evaluate imaging ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108: 20719–20724, 2011. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK-94199/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK104211/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-97829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-68854/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-62641/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-68764/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-89538/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-92758/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-72473/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK094199/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-104211/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-69603/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-66636/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-89572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-63439/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

