IL-6-driven STAT signalling in circulating CD4+ lymphocytes is a marker for early anticitrullinated peptide antibody-negative rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 25649145
- PMCID: PMC4752669
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205850
IL-6-driven STAT signalling in circulating CD4+ lymphocytes is a marker for early anticitrullinated peptide antibody-negative rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objectives: A previously identified signal transduction and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) target-enriched gene signature in circulating CD4+ T cells of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) was prominent in autoantibody-negative individuals. Here, interleukin (IL)-6-mediated STAT signalling was investigated in circulating lymphocytes of an independent early arthritis patient cohort, seeking further insight into RA pathogenesis and biomarkers of potential clinical utility.
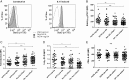
Methods: Constitutive and IL-6-induced expression of phosphorylated STAT1 (pSTAT1) and pSTAT3 was determined in T and B cells using Phosflow cytometric analysis in patients with RA and controls. Contemporaneous levels of serum cytokines were measured by immunoassay. Induced gene expression was measured in cultured CD4+T cells by quantitative real-time PCR.
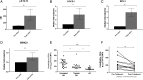
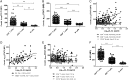
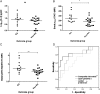
Results: Among circulating lymphocytes of 187 patients with early arthritis, constitutive pSTAT3 correlated with serum IL-6 levels maximally in CD4+ T cells. Increased constitutive pSTAT3, but not pSTAT1, was observed in circulating CD4+ T cells of patients with early anticitrullinated peptide autoantibody (ACPA)-negative RA compared with disease controls, and these levels decreased alongside markers of disease activity with IL-6R-targeted treatment. Among patients presenting with seronegative undifferentiated arthritis (UA) the ratio of constitutive pSTAT3:pSTAT1 in CD4+ T cells contributed substantially to an algorithm for predicting progression to classifiable RA during a median of 20 months follow-up (area under receiver operator characteristic curve=0.84; p<0.001).
Conclusions: Our findings support a particular role for IL-6-driven CD4+ T cell activation via STAT3 during the induction of RA, particularly as a feature of ACPA-negative disease. CD4+ T cell pSTAT measurements show promise as biomarkers of UA-RA progression and now require independent validation.
Keywords: Cytokines; Early Rheumatoid Arthritis; T Cells.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures

Similar articles
-
A CD4 T cell gene signature for early rheumatoid arthritis implicates interleukin 6-mediated STAT3 signalling, particularly in anti-citrullinated peptide antibody-negative disease.Ann Rheum Dis. 2012 Aug;71(8):1374-81. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200968. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012. PMID: 22532634 Free PMC article.
-
The activity of JAK-STAT pathways in rheumatoid arthritis: constitutive activation of STAT3 correlates with interleukin 6 levels.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015 Jun;54(6):1103-13. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu430. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015. PMID: 25406356
-
Constitutive STAT3 Phosphorylation in Circulating CD4+ T Lymphocytes Associates with Disease Activity and Treatment Response in Recent-Onset Rheumatoid Arthritis.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 9;10(9):e0137385. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137385. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26353115 Free PMC article.
-
Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenetic and therapeutic aspects.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2014 Aug;28(4):651-9. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2014.10.016. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 25481556 Review.
-
A core set of risk factors in individuals at risk of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review informing the EULAR points to consider for conducting clinical trials and observational studies in individuals at risk of rheumatoid arthritis.RMD Open. 2021 Sep;7(3):e001768. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-001768. RMD Open. 2021. PMID: 34531306 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regulatory role of miRNA-26a in neonatal sepsis.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Dec;16(6):4836-4842. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6779. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30542439 Free PMC article.
-
Diminished cytokine-induced Jak/STAT signaling is associated with rheumatoid arthritis and disease activity.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 14;16(1):e0244187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244187. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33444321 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent inflammatory and non-inflammatory mechanisms in refractory rheumatoid arthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021 Jan;17(1):17-33. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-00541-7. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33293696 Review.
-
Expression of STAT3-regulated genes in circulating CD4+ T cells discriminates rheumatoid arthritis independently of clinical parameters in early arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019 Jul 1;58(7):1250-1258. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez003. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 30753680 Free PMC article.
-
A case of effective tocilizumab for arthropathy due to dialysis-related amyloidosis.CEN Case Rep. 2025 Jun 26. doi: 10.1007/s13730-025-01009-x. Online ahead of print. CEN Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40571902
References
-
- Pratt AG, Swan DC, Richardson S, et al. . A CD4T cell gene signature for early rheumatoid arthritis implicates interleukin 6-mediated STAT3 signalling, particularly in anti-citrullinated peptide antibody-negative disease. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:1374–81. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200968 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Emery P, Keystone E, Tony HP, et al. . IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: results from a 24-week multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial.[Erratum appears in Ann Rheum Dis 2009;68:296]. Ann Rheum Dis 2008;67:1516–23. 10.1136/ard.2008.092932 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

