Neurovascular control following small muscle-mass exercise in humans
- PMID: 25649250
- PMCID: PMC4393198
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.12289
Neurovascular control following small muscle-mass exercise in humans
Abstract
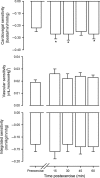
Sustained postexercise vasodilation, which may be mediated at both a neural and vascular level, is seen in previously active skeletal muscle vascular beds following both large and small muscle-mass exercise. Blunted sympathetic vascular transduction and a downward resetting of the arterial baroreflex contribute to this vasodilation after cycling (large muscle-mass exercise), but it is unknown if these responses also contribute to sustained vasodilation following small muscle-mass exercise. This study aimed to determine if baroreflex sensitivity is altered, the baroreflex is reset, or if sympathetic vascular transduction is blunted following small muscle-mass exercise. Eleven healthy, college-aged subjects (five males, six females) completed one-leg dynamic knee-extension exercise for 1 h at 60% of peak power output. While cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity was increased ~23% postexercise relative to preexercise (P < 0.05), vascular and integrated baroreflex sensitivity were not altered following exercise (P = 0.31 and P = 0.48). The baroreflex did not exhibit resetting (P > 0.69), and there was no evidence of changes in vascular transduction following exercise (P = 0.73). In conclusion, and in contrast to large muscle-mass exercise, it appears that small muscle-mass exercise produces a sustained postexercise vasodilation that is largely independent of central changes in the baroreflex.
Keywords: Dynamic knee extension, baroreflex; exercise; neurovascular; postexercise hypotension; sympathetic; transduction.
© 2015 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Physiological Society and The Physiological Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regional hemodynamics during postexercise hypotension. I. Splanchnic and renal circulations.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2004 Dec;97(6):2065-70. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00465.2004. Epub 2004 Aug 13. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2004. PMID: 15310744
-
Carotid baroreflex control of central and peripheral hemodynamics during recovery after moderate leg cycling exercise.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020 Jun 1;128(6):1477-1486. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00023.2020. Epub 2020 Apr 30. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020. PMID: 32352342
-
Postexercise hypotension and sustained postexercise vasodilatation: what happens after we exercise?Exp Physiol. 2013 Jan;98(1):7-18. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2011.058065. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Exp Physiol. 2013. PMID: 22872658 Review.
-
Impaired sympathetic vascular regulation in humans after acute dynamic exercise.J Physiol. 1996 Aug 15;495 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):279-88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021592. J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8866370 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial baroreflex control of the peripheral vasculature in humans: rest and exercise.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008 Dec;40(12):2055-62. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e318180bc80. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008. PMID: 18981944 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Time of Day on Sustained Postexercise Vasodilation Following Small Muscle-Mass Exercise in Humans.Front Physiol. 2019 Jun 25;10:762. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00762. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31293439 Free PMC article.
-
The cardiovascular system after exercise.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017 Apr 1;122(4):925-932. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00802.2016. Epub 2017 Feb 2. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017. PMID: 28153943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mast cell degranulation and de novo histamine formation contribute to sustained postexercise vasodilation in humans.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017 Mar 1;122(3):603-610. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00633.2016. Epub 2016 Aug 25. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017. PMID: 27562843 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Central and peripheral modulation of exercise pressor reflex sensitivity after nonfatiguing work.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2020 Nov 1;319(5):R575-R583. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00127.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32877237 Free PMC article.
-
Vasodilator function is impaired in burn injury survivors.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):R1054-R1060. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00188.2018. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30256680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baecke JAH, Burema J. Frijters JER. A short questionnaire for the measurement of habitual physical activity in epidemiological studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1982;36:936–942. - PubMed
-
- Barrett-O'Keefe Z, Kaplon RE. Halliwill JR. Sustained postexercise vasodilatation and histamine receptor activation following small muscle-mass exercise in humans. Exp. Physiol. 2013;98:268–277. - PubMed
-
- Brown T, Beightol L, Koh J. Eckberg DL. Important influence of respiration on human RR interval power spectra is largely ignored. J. Appl. Physiol. 1993;75:2310–2317. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

