Decolorization and detoxification of sulfonated toxic diazo dye C.I. Direct Red 81 by Enterococcus faecalis YZ 66
- PMID: 25649265
- PMCID: PMC4299565
- DOI: 10.1186/s40201-014-0151-1
Decolorization and detoxification of sulfonated toxic diazo dye C.I. Direct Red 81 by Enterococcus faecalis YZ 66
Abstract
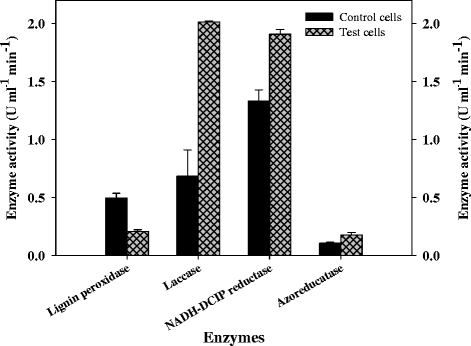
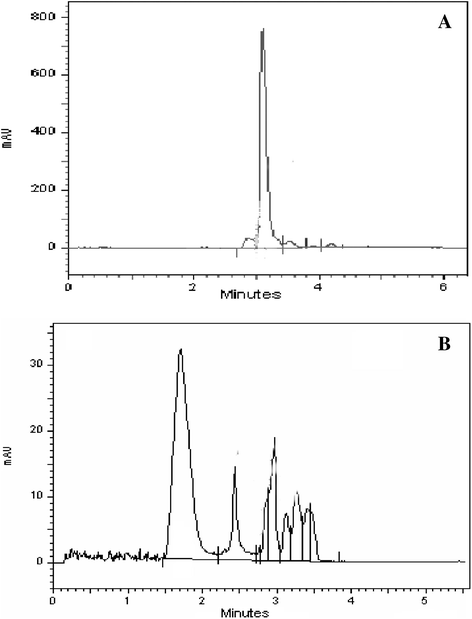
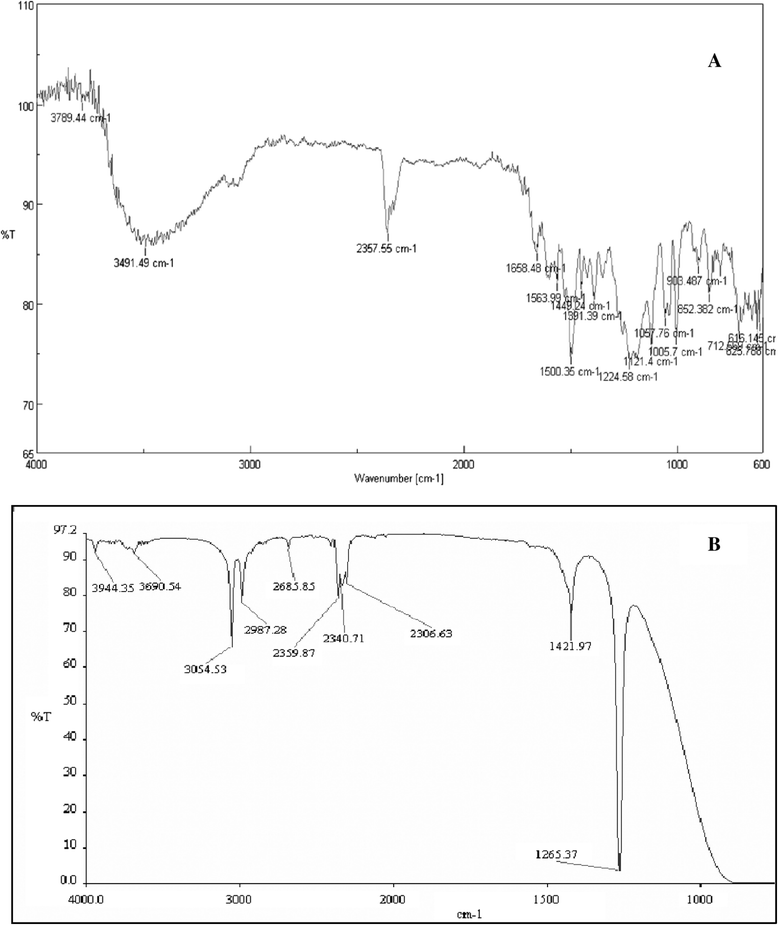
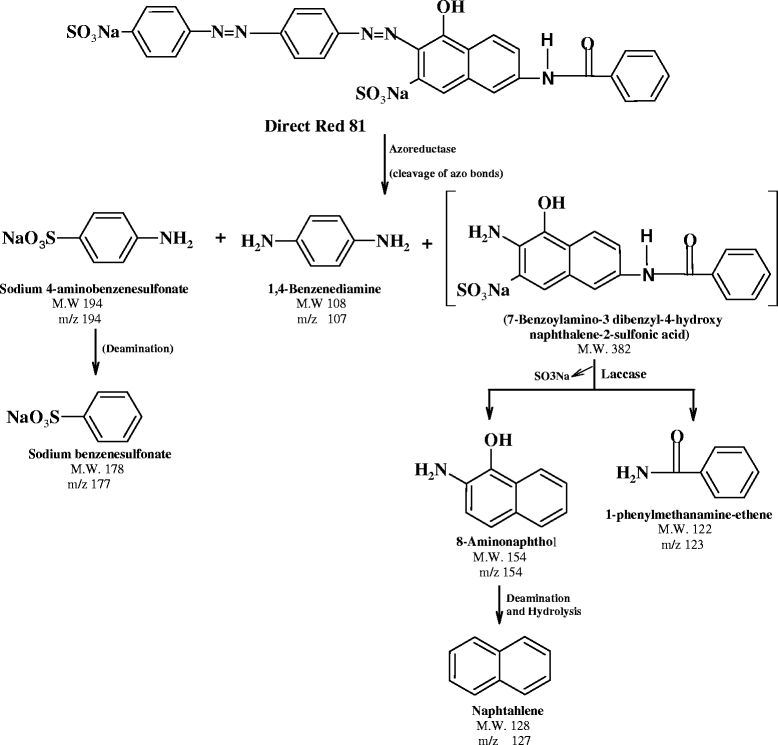
Isolated Enterococcus faecalis YZ 66 strain shows ability to decolorize various industrial dyes among which, it showed complete decolorization and degradation of toxic, sulfonated recalcitrant diazo dye Direct Red 81 (50 mg/L) within 1.5 h of incubation under static anoxic condition. The optimum pH and temperature for decolorization was 7.0 and 40°C, respectively. Significant induction in the activity of intracellular oxidoreductive enzymes suggested its involvement in the decolorization of Direct Red 81. The biodegradation of Direct Red 81 was monitored by UV-Visible, FT-IR spectroscopy and HPLC. The final products were characterized by GC-MS and possible pathway of the degradation of the dye was proposed. The phytotoxicity assay (with respect to plants Sorghum vulgare and Phaseolus mungo) revealed that the degradation of Direct Red 81 produced nontoxic metabolites. Finally E. faecalis was employed to decolorize actual industrial effluent showing decolorization (in terms of ADMI value) with moderate COD and BOD reduction. Moreover the result increases the applicability of the strain for the treatment of industrial wastewaters containing dye pollutants.
Keywords: ABTS; ADMI; Azoreductase; Direct Red 81; Enterococcus faecalis; GC-MS; Lignin peroxidase.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Decolorization and detoxification of sulfonated azo dye C.I. Remazol Red and textile effluent by isolated Lysinibacillus sp. RGS.J Biosci Bioeng. 2013 Jun;115(6):658-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2012.12.009. Epub 2013 Jan 12. J Biosci Bioeng. 2013. PMID: 23321576
-
Ecofriendly biodegradation and detoxification of Reactive Red 2 textile dye by newly isolated Pseudomonas sp. SUK1.J Hazard Mater. 2009 Apr 30;163(2-3):735-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.020. Epub 2008 Jul 12. J Hazard Mater. 2009. PMID: 18718713
-
Decolorization and detoxification of sulfonated azo dye methyl orange by Kocuria rosea MTCC 1532.J Hazard Mater. 2010 Apr 15;176(1-3):503-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.058. Epub 2009 Nov 13. J Hazard Mater. 2010. PMID: 19969416
-
Ecofriendly degradation of sulfonated diazo dye C.I. Reactive Green 19A using Micrococcus glutamicus NCIM-2168.Bioresour Technol. 2009 Sep;100(17):3897-905. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.03.051. Epub 2009 Apr 17. Bioresour Technol. 2009. PMID: 19375909
-
An Integrative Approach to Study Bacterial Enzymatic Degradation of Toxic Dyes.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jan 28;12:802544. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.802544. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35154033 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Azoreductase activity of dye-decolorizing bacteria isolated from the human gut microbiota.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 2;9(1):5508. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41894-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30940826 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation of Direct Red 81 mediated by Fenton reactions: multivariate optimization, effect of chloride and sulfate, and acute ecotoxicity assessment.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Mar;24(7):6176-6186. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6977-6. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 27255315
-
Characterization and optimization of azo dyes degrading microbes isolated from textile effluent.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 2;15(1):11241. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95359-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40175441 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation and Toxicity Analysis of a Reactive Textile Diazo Dye-Direct Red 81 by Newly Isolated Bacillus sp. DMS2.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 24;11:576680. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.576680. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33072041 Free PMC article.
-
Biodecolorization and Biodegradation of Azo Dye Reactive Orange-16 by Marine Nocardiopsis sp.Iran J Biotechnol. 2019 Sep 1;17(3):e1551. doi: 10.29252/ijb.1551. eCollection 2019 Sep. Iran J Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 32195279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jirasripongpun K, Rujikan N, Jongjira N, Boonsiri C. Decolorization and degradation of C.I. Reactive Red 195 by Enterobacter sp. Thammasat Int J Sci Technol. 2007;12:6–11.
-
- Keharia H, Patel H, Madamwar D. Decolorization screening of synthetic dyes by anaerobic, methanogenic sludge using batch decolourization assay. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004;20:365–370. doi: 10.1023/B:WIBI.0000033056.42908.93. - DOI
-
- Kodam KM, Soojhawon I, Lokhande PD, Gawai KR. Microbial decolorization of reactive azo dyes under aerobic conditions. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2005;21:367–370. doi: 10.1007/s11274-004-5957-z. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

