FOXP1 potentiates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- PMID: 25650440
- PMCID: PMC4356208
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.2005654
FOXP1 potentiates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Abstract
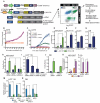
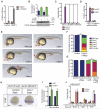
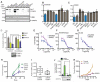
The transcription factor FOXP1 (forkhead box protein P1) is a master regulator of stem and progenitor cell biology. In diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), copy number amplifications and chromosomal translocations result in overexpression of FOXP1. Increased abundance of FOXP1 in DLBCL is a predictor of poor prognosis and resistance to therapy. We developed a genome-wide, mass spectrometry-coupled, gain-of-function genetic screen, which revealed that FOXP1 potentiates β-catenin-dependent, Wnt-dependent gene expression. Gain- and loss-of-function studies in cell models and zebrafish confirmed that FOXP1 was a general and conserved enhancer of Wnt signaling. In a Wnt-dependent fashion, FOXP1 formed a complex with β-catenin, TCF7L2 (transcription factor 7-like 2), and the acetyltransferase CBP [CREB (adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate response element-binding protein)-binding protein], and this complex bound the promoters of Wnt target genes. FOXP1 promoted the acetylation of β-catenin by CBP, and acetylation was required for FOXP1-mediated potentiation of β-catenin-dependent transcription. In DLBCL, we found that FOXP1 promoted sensitivity to Wnt pathway inhibitors, and knockdown of FOXP1 or blocking β-catenin transcriptional activity slowed xenograft tumor growth. These data connect excessive FOXP1 with β-catenin-dependent signal transduction and provide a molecular rationale for Wnt-directed therapy in DLBCL.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
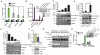

References
-
- Anastas JN, Moon RT. WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nature reviews. Cancer. 2013;13:11–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

