Efficacy of a device to narrow the coronary sinus in refractory angina
- PMID: 25651246
- PMCID: PMC6647842
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1402556
Efficacy of a device to narrow the coronary sinus in refractory angina
Abstract
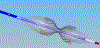
Background: Many patients with coronary artery disease who are not candidates for revascularization have refractory angina despite standard medical therapy. The balloon-expandable, stainless steel, hourglass-shaped, coronary-sinus reducing device creates a focal narrowing and increases pressure in the coronary sinus, thus redistributing blood into ischemic myocardium.
Methods: We randomly assigned 104 patients with Canadian Cardiovascular Society (CCS) class III or IV angina (on a scale from I to IV, with higher classes indicating greater limitations on physical activity owing to angina) and myocardial ischemia, who were not candidates for revascularization, to implantation of the device (treatment group) or to a sham procedure (control group). The primary end point was the proportion of patients with an improvement of at least two CCS angina classes at 6 months.
Results: A total of 35% of the patients in the treatment group (18 of 52 patients), as compared with 15% of those in the control group (8 of 52), had an improvement of at least two CCS angina classes at 6 months (P=0.02). The device was also associated with improvement of at least one CCS angina class in 71% of the patients in the treatment group (37 of 52 patients), as compared with 42% of those in the control group (22 of 52) (P=0.003). Quality of life as assessed with the use of the Seattle Angina Questionnaire was significantly improved in the treatment group, as compared with the control group (improvement on a 100-point scale, 17.6 vs. 7.6 points; P=0.03). There were no significant between-group differences in improvement in exercise time or in the mean change in the wall-motion index as assessed by means of dobutamine echocardiography. At 6 months, 1 patient in the treatment group had had a myocardial infarction; in the control group, 1 patient had died and 3 had had a myocardial infarction.
Conclusions: In this small clinical trial, implantation of the coronary-sinus reducing device was associated with significant improvement in symptoms and quality of life in patients with refractory angina who were not candidates for revascularization. (Funded by Neovasc; COSIRA ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01205893.).
Figures



Comment in
-
Potential relief for refractory angina.N Engl J Med. 2015 Feb 5;372(6):566-7. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1413941. N Engl J Med. 2015. PMID: 25651252 No abstract available.
-
Coronary artery disease: Interventional narrowing of the coronary sinus in refractory angina.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015 Apr;12(4):196. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.19. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25687777 No abstract available.
-
A device to narrow the coronary sinus for angina.N Engl J Med. 2015 May 14;372(20):1967-8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1503672. N Engl J Med. 2015. PMID: 25970058 No abstract available.
-
A device to narrow the coronary sinus for angina.N Engl J Med. 2015 May 14;372(20):1965-6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1503672. N Engl J Med. 2015. PMID: 25970059 No abstract available.
-
A device to narrow the coronary sinus for angina.N Engl J Med. 2015 May 14;372(20):1966. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1503672. N Engl J Med. 2015. PMID: 25970060 No abstract available.
-
A device to narrow the coronary sinus for angina.N Engl J Med. 2015 May 14;372(20):1966-7. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1503672. N Engl J Med. 2015. PMID: 25970061 No abstract available.
-
A device to narrow the coronary sinus for angina.N Engl J Med. 2015 May 14;372(20):1967. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1503672. N Engl J Med. 2015. PMID: 25970062 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fihn SD, Gardin JM, Abrams J et al. 2012 ACCF/AHA/ACP/AATS/PCNA/SCAI/STS Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Patients With Stable Ischemic Heart Disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012.
-
- Jolicoeur EM, Granger CB, Henry TD, Holmes DJ, Pepine CJ, Mark D, Chaitman BR, Gersh BJ, Ohman EM. Clinical and research issues regarding chronic advanced coronary artery disease: part I: Contemporary and emerging therapies. Am Heart J 2008;155(3):418–434. - PubMed
-
- Williams B, Menon M, Satran D, Hayward D, Hodges JS, Burke MN, Johnson RK, Poulose AK, Traverse JH, Henry TD. Patients with coronary artery disease not amenable to traditional revascularization: prevalence and 3-year mortality. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 2010;75(6):886–891. - PubMed
-
- Banai S, Ben Muvhar S, Parikh KH, Medina A, Sievert H, Seth A, Tsehori J, Paz Y, Sheinfeld A, Keren G. Coronary sinus reducer stent for the treatment of chronic refractory angina pectoris: a prospective, open-label, multicenter, safety feasibility first-in-man study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;49(17):1783–1789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
