Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography, FibroScan®, Forns' index and their combination in the assessment of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B, and the impact of inflammatory activity and steatosis on these diagnostic methods
- PMID: 25651500
- PMCID: PMC4394958
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3299
Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography, FibroScan®, Forns' index and their combination in the assessment of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B, and the impact of inflammatory activity and steatosis on these diagnostic methods
Abstract
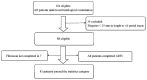
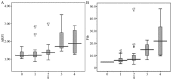
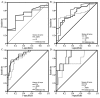
The aim of the present study was to investigate the combination of certain serological markers (Forns' index; FI), FibroScan® and acoustic radiation force impulse elastography (ARFI) in the assessment of liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis B, and to explore the impact of inflammatory activity and steatosis on the accuracy of these diagnostic methods. Eighty‑one patients who had been diagnosed with hepatitis B were recruited and the stage of fibrosis was determined by biopsy. The diagnostic accuracy of FI, FibroScan and ARFI, as well as that of the combination of these methods, was evaluated based on the conformity of the results from these tests with those of biopsies. The effect of concomitant inflammation on diagnostic accuracy was also investigated by dividing the patients into two groups based on the grade of inflammation (G<2 and G≥2). The overall univariate correlation between steatosis and the diagnostic value of the three methods was also evaluated. There was a significant association between the stage of fibrosis and the results obtained using ARFI and FibroScan (Kruskal‑Wallis; P<0.001 for all patients), and FI (t-test, P<0.001 for all patients). The combination of FI with ARFI/FibroScan increased the predictive accuracy with a fibrosis stage of S≥2 or cirrhosis. There was a significant correlation between the grade of inflammation and the results obtained using ARFI and FibroScan (Kruskal‑Wallis, P<0.001 for all patients), and FI (t-test; P<0.001 for all patients). No significant correlation was detected between the measurements obtained using ARFI, FibroScan and FI, and steatosis (r=‑0.100, P=0.407; r=0.170, P=0.163; and r=0.154, P=0.216, respectively). ARFI was shown to be as effective in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis as FibroScan or FI, and the combination of ARFI or FibroScan with FI may improve the accuracy of diagnosis. The presence of inflammatory activity, but not that of steatosis, may affect the diagnostic accuracy of these methods.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis with impulse elastography: comparison of Supersonic Shear Imaging with ARFI and FibroScan®.J Hepatol. 2014 Sep;61(3):550-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.04.044. Epub 2014 May 9. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24815876
-
Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B.J Viral Hepat. 2013 Apr;20(4):240-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2012.01646.x. Epub 2012 Jul 31. J Viral Hepat. 2013. PMID: 23490368
-
Evaluation of liver fibrosis by transient elastography using acoustic radiation force impulse: comparison with Fibroscan(®).J Gastroenterol. 2011 Oct;46(10):1238-48. doi: 10.1007/s00535-011-0437-3. Epub 2011 Jul 21. J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21779759
-
Meta-analysis: ARFI elastography versus transient elastography for the evaluation of liver fibrosis.Liver Int. 2013 Sep;33(8):1138-47. doi: 10.1111/liv.12240. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Liver Int. 2013. PMID: 23859217 Review.
-
Transient Elastography for Assessment of Liver Fibrosis and Steatosis: An Evidence-Based Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2015 Nov 1;15(18):1-45. eCollection 2015. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2015. PMID: 26664664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound score combined with liver stiffness measurement by sound touch elastography for staging liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: a clinical prospective study.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Mar;10(6):271. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-505. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35434021 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Elastography Methods in Liver Disease: Current Evidence and Future Directions.Radiology. 2018 Mar;286(3):738-763. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018170601. Radiology. 2018. PMID: 29461949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual-etiology MAFLD: the interactions between viral hepatitis B, viral hepatitis C, alcohol, and MAFLD.Hepatol Int. 2024 Oct;18(Suppl 2):897-908. doi: 10.1007/s12072-024-10699-x. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Hepatol Int. 2024. PMID: 39115632 Review.
-
Evaluation of APRI and FIB-4 for noninvasive assessment of significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in HBeAg-negative CHB patients with ALT ≤ 2 ULN: A retrospective cohort study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Mar;96(12):e6336. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006336. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28328813 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound—New Techniques Are Extending the Applications.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2023 Jan 27;120(4):41-47. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.m2022.0380. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2023. PMID: 36519209 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

