MMP-12-mediated by SARM-TRIF signaling pathway contributes to IFN-γ-independent airway inflammation and AHR post RSV infection in nude mice
- PMID: 25652021
- PMCID: PMC4332892
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-015-0176-8
MMP-12-mediated by SARM-TRIF signaling pathway contributes to IFN-γ-independent airway inflammation and AHR post RSV infection in nude mice
Abstract
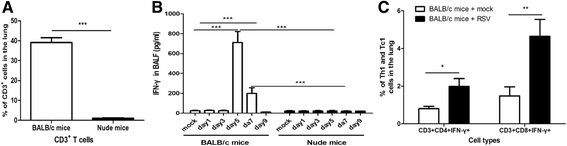
Background: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is one of the most frequently observed pathogens during infancy and childhood. However, the corresponding pathogenesis has not been determined to date. We previously demonstrated that IFN-γ plays an important role in RSV pathogenesis, and SARM-TRIF-signaling pathway could regulate the production of IFN-γ. This study is to investigate whether T cells or innate immune cells are the predominant producers of IFN-γ, and further to explore other culprits in addition to IFN-γ in the condition of RSV infection.
Methods: Normal BALB/c mice and nude mice deficient in T cells were infected intranasally with RSV. Leukocytes in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were counted, lung histopathology was examined, and airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) was measured by whole-body plethysmography. IFN-γ and MMP-12 were detected by ELISA. MMP408, a selective MMP-12 inhibitor, was given intragastrically. Resveratrol, IFN-γ neutralizing antibody and recombinant murine IFN-γ were administered intraperitoneally. SARM and TRIF protein were semi-quantified by Western blot. siRNA was used to knock-down SARM expression.
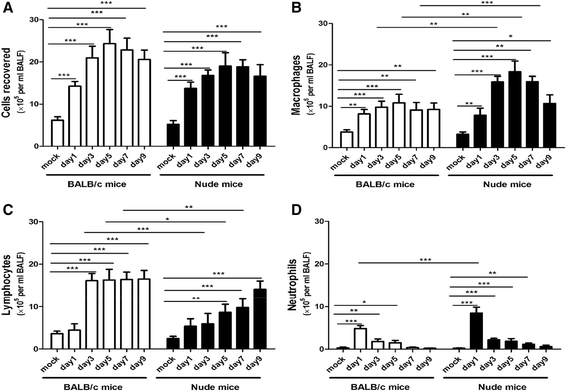
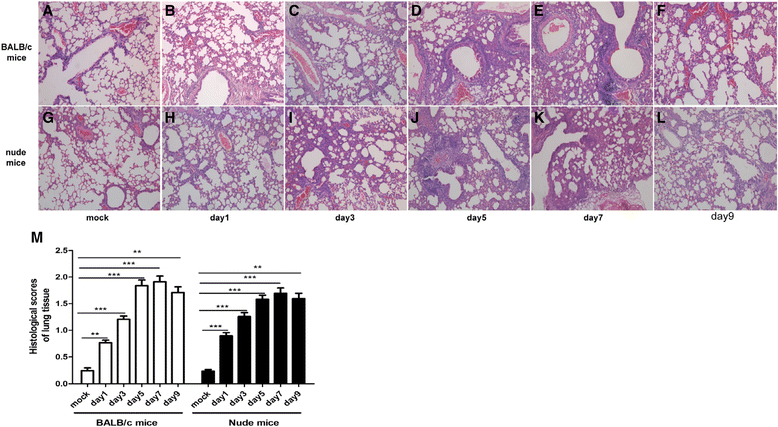
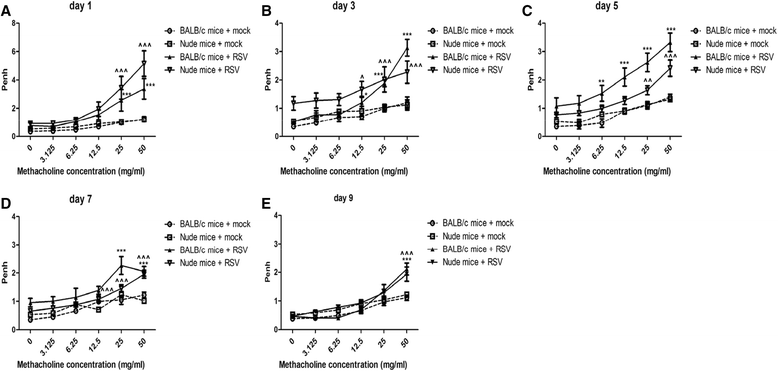
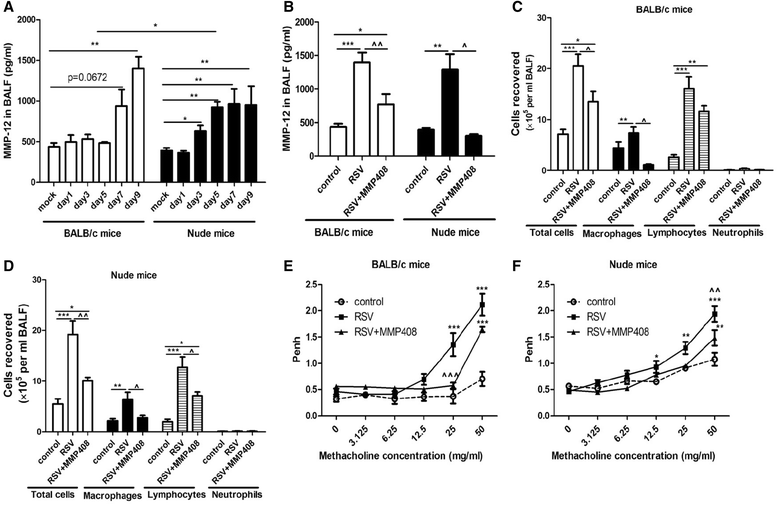
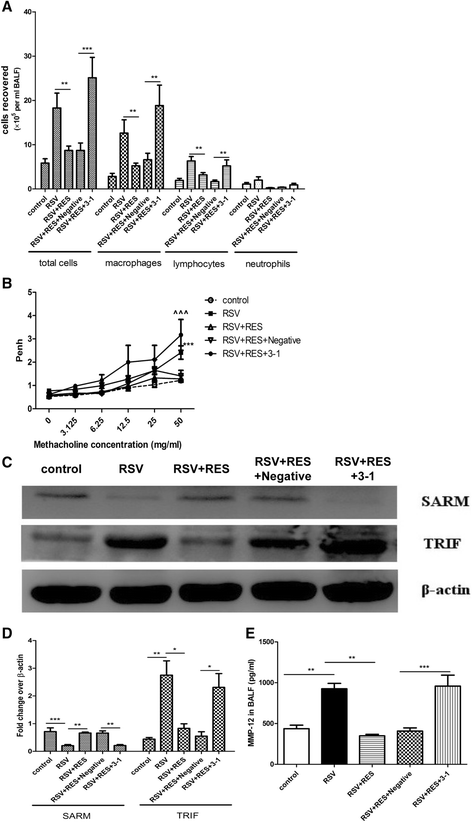
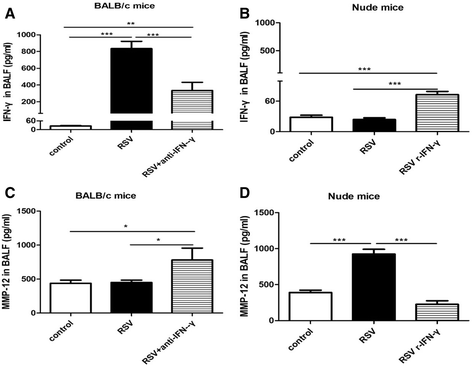
Results: RSV induced significant airway inflammation and AHR in both mice; IFN-γ was significantly increased in BALB/c mice but not in nude mice. MMP-12 was dramatically increased in both mice but earlier in nude mice. When MMP-12 was inhibited by MMP408, RSV-induced respiratory symptoms were alleviated. SARM was significantly suppressed while TRIF was significantly enhanced in both mice strains. Following resveratrol administration in nude mice, 1) SARM inhibition was prevented, 2) TRIF and MMP-12 were correspondingly down-regulated and 3) airway disorders were subsequently alleviated. Moreover, when SARM was efficiently knocked down using siRNA, TRIF and MMP-12 were markedly enhanced, and the anti-RSV effects of resveratrol were remarkably abrogated. MMP-12 was significantly increased in the IFN-γ neutralizing antibody-treated BALB/c mice but reduced in the recombinant murine IFN-γ-treated nude mice.
Conclusions: MMP-12 can result in at least part of the airway inflammation and AHR independent of IFN-γ. And SARM-TRIF- signaling pathway is involved in regulating the overproduction of MMP-12. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first that has examined the effects of SARM on MMP-12 and further highlights the potential to target SARM-TRIF-MMP-12 cascades to treat RSV infection.
Figures
References
-
- Liu T, Zang N, Zhou N, Li W, Xie X, Deng Y, et al. Resveratrol inhibits the TRIF-dependent pathway by upregulating sterile alpha and armadillo motif protein, contributing to anti-inflammatory effects after respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Virol. 2014;88:4229–4236. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03637-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zang N, Xie X, Deng Y, Wu S, Wang L, Peng C, et al. Resveratrol-mediated gamma interferon reduction prevents airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in respiratory syncytial virus-infected immunocompromised mice. J Virol. 2011;85:13061–13068. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05869-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

