The GPR55 agonist lysophosphatidylinositol relaxes rat mesenteric resistance artery and induces Ca(2+) release in rat mesenteric artery endothelial cells
- PMID: 25652040
- PMCID: PMC4459022
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13107
The GPR55 agonist lysophosphatidylinositol relaxes rat mesenteric resistance artery and induces Ca(2+) release in rat mesenteric artery endothelial cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: Lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI), a lipid signalling molecule, activates GPR55 and elevates intracellular Ca(2+). Here, we examine the actions of LPI in the rat resistance mesenteric artery and Ca(2+) responses in endothelial cells isolated from the artery.
Experimental approach: Vascular responses were studied using wire myographs. Single-cell fluorescence imaging was performed using a MetaFluor system. Hypotensive effects of LPI were assessed using a Biopac system.
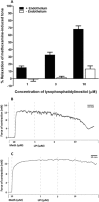
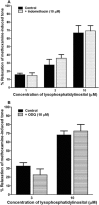
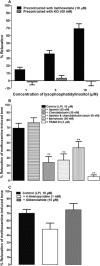
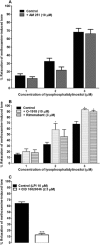
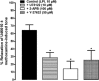
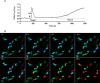
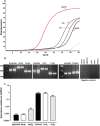
Key results: In isolated arteries, LPI-induced vasorelaxation was concentration- and endothelium-dependent and inhibited by CID 16020046, a GPR55 antagonist. The CB1 receptor antagonist AM 251 had no effect, whereas rimonabant and O-1918 significantly potentiated LPI responses. Vasorelaxation was reduced by charybdotoxin and iberiotoxin, alone or combined. LPI decreased systemic arterial pressure. GPR55 is expressed in rat mesenteric artery. LPI caused biphasic elevations of endothelial cell intracellular Ca(2+). Pretreatment with thapsigargin or 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate abolished both phases. The PLC inhibitor U73122 attenuated the initial phase and enhanced the second phase, whereas the Rho-associated kinase inhibitor Y-27632 abolished the late phase but not the early phase.
Conclusions and implications: LPI is an endothelium-dependent vasodilator in the rat small mesenteric artery and a hypotensive agent. The vascular response involves activation of Ca(2+)-sensitive K(+) channels and is not mediated by CB1 receptors, but unexpectedly enhanced by antagonists of the 'endothelial anandamide' receptor. In endothelial cells, LPI utilizes PLC-IP3 and perhaps ROCK-RhoA pathways to elevate intracellular Ca(2+). Overall, these findings support an endothelial site of action for LPI and suggest a possible role for GPR55 in vasculature.
© 2015 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- AlSuleimani YM. 2011. PhD thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK An investigation into the actions of novel lipid signalling molecules in the vasculature.
-
- AlSuleimani YM, Hiley CR. Mechanisms of vasorelaxation induced by oleoylethanolamide in the rat small mesenteric artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;702:1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

