Evidence that FcRn mediates the transplacental passage of maternal IgE in the form of IgG anti-IgE/IgE immune complexes
- PMID: 25652137
- PMCID: PMC4437844
- DOI: 10.1111/cea.12508
Evidence that FcRn mediates the transplacental passage of maternal IgE in the form of IgG anti-IgE/IgE immune complexes
Abstract
Background: The mechanism(s) responsible for acquisition of maternal antibody isotypes other than IgG are not fully understood. This uncertainty is a major reason underlying the continued controversy regarding whether cord blood (CB) IgE originates in the mother or fetus.
Objective: To investigate the capacity of maternal IgE to be transported across the placenta in the form of IgG anti-IgE/IgE immune complexes (ICs) and to determine the role of the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) in mediating this process.
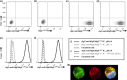
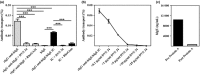
Methods: Maternal and CB serum concentrations of IgE, IgG anti-IgE, and IgG anti-IgE/IgE ICs were determined in a cohort of allergic and non-allergic mother/infant dyads. Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells stably transfected with human FcRn were used to study the binding and transcytosis of IgE in the form of IgG anti-IgE/IgE ICs.
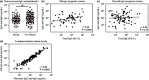
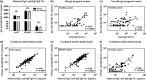
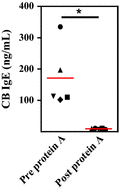
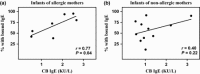
Results: Maternal and CB serum concentrations of IgG anti-IgE/IgE ICs were highly correlated, regardless of maternal allergic status. IgG anti-IgE/IgE ICs generated in vitro bound strongly to FcRn-expressing MDCK cells and were transcytosed in an FcRn-dependent manner. Conversely, monomeric IgE did not bind to FcRn and was not transcytosed. IgE was detected in solutions of transcytosed IgG anti-IgE/IgE ICs, even though essentially all the IgE remained in complex form. Similarly, the majority of IgE in CB sera was found to be complexed to IgG.
Conclusions and clinical relevance: These data indicate that human FcRn facilitates the transepithelial transport of IgE in the form of IgG anti-IgE/IgE ICs. They also strongly suggest that the majority of IgE in CB sera is the result of FcRn-mediated transcytosis of maternal-derived IgG anti-IgE/IgE ICs. These findings challenge the widespread perception that maternal IgE does not cross the placenta. Measuring maternal or CB levels of IgG anti-IgE/IgE ICs may be a more accurate predictor of allergic risk.
Keywords: FcRn; IgG anti-IgE; allergy; autoantibodies; cord blood; immune complexes; infant; mother; placenta.
© 2015 The Authors. Clinical & Experimental Allergy Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Comment in
-
Cord blood IgE: fetal or maternal?Clin Exp Allergy. 2015 Jun;45(6):1012-4. doi: 10.1111/cea.12530. Clin Exp Allergy. 2015. PMID: 25981350 No abstract available.
References
-
- Avrech OM, Samra Z, Lazarovich Z, Caspi E, Jacobovich A, Sompolinsky D. Efficacy of the placental barrier for immunoglobulins: correlations between maternal, paternal and fetal immunoglobulin levels. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 1994; 103:160–5. - PubMed
-
- Holt PG. Prenatal versus postnatal priming of allergen specific immunologic memory: the debate continues. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 122:717–8. - PubMed
-
- Simister NE, Story CM, Chen HL, Hunt JS. An IgG‐transporting Fc receptor expressed in the syncytiotrophoblast of human placenta. Eur J Immunol 1996; 26:1527–31. - PubMed
-
- Firan M, Bawdon R, Radu C et al The MHC class I‐related receptor, FcRn, plays an essential role in the maternofetal transfer of gamma‐globulin in humans. Int Immunol 2001; 13:993–1002. - PubMed
-
- Israel EJ, Patel VK, Taylor SF, Marshak‐Rothstein A, Simister NE. Requirement for a beta 2‐microglobulin‐associated Fc receptor for acquisition of maternal IgG by fetal and neonatal mice. J Immunol 1995; 154:6246–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

