Denatonium inhibits growth and induces apoptosis of airway epithelial cells through mitochondrial signaling pathways
- PMID: 25652218
- PMCID: PMC4326484
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-015-0183-9
Denatonium inhibits growth and induces apoptosis of airway epithelial cells through mitochondrial signaling pathways
Abstract
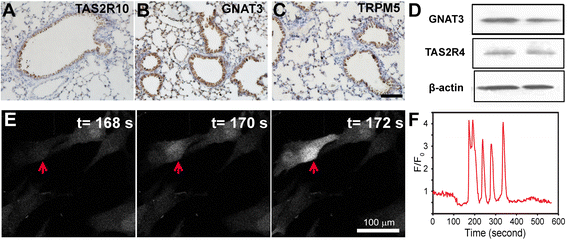
Background: Denatonium, a widely used bitter agonist, activates bitter taste receptors on many cell types and plays important roles in chemical release, ciliary beating and smooth muscle relaxation through intracellular Ca(2+)-dependent pathways. However, the effects of denatonium on the proliferation of airway epithelial cells and on the integrity of cellular components such as mitochondria have not been studied. In this study, we hypothesize that denatonium might induce airway epithelial cell injury by damaging mitochondria.
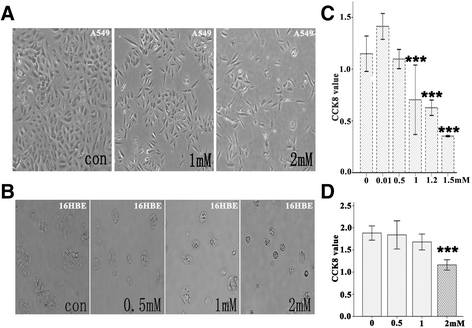
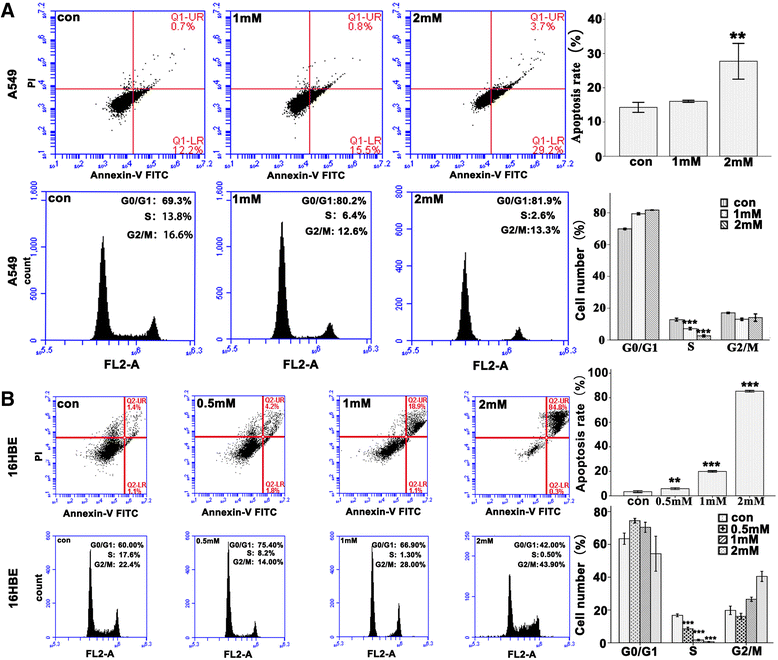
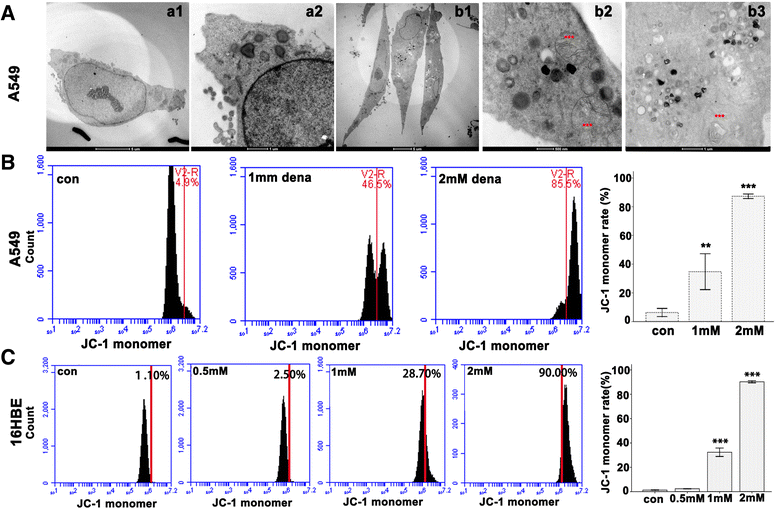
Methods: Bright-field microscopy, cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay and flow cytometry analysis were used to examine cellular morphology, proliferation and cell cycle, respectively. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was used to examine mitochondrial integrity. JC-1 dye and western blotting techniques were used to measure mitochondrial membrane potential and protein expression, respectively.
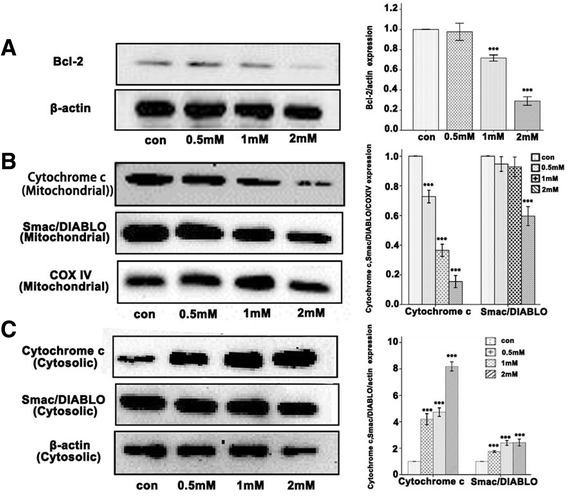
Results: For airway epithelial cells, we observed that denatonium significantly effects cellular morphology, decreases cell proliferation and reduces the number of cells in S phase in a dose-dependent manner. TEM analysis demonstrated that denatonium causes large amplitude swelling of mitochondria, which was confirmed by the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, the down-regulation of Bcl-2 protein and the subsequent enhancement of the mitochondrial release of cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO after denatonium treatment.
Conclusions: In this study, we demonstrated for the first time that denatonium damages mitochondria and thus induces apoptosis in airway epithelial cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Melittin induces human gastric cancer cell apoptosis via activation of mitochondrial pathway.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Mar 21;22(11):3186-95. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i11.3186. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27003995 Free PMC article.
-
Denatonium as a bitter taste receptor agonist damages jejunal epithelial cells of yellow-feathered chickens via inducing apoptosis.Animal. 2020 Jun;14(6):1223-1233. doi: 10.1017/S1751731119002994. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Animal. 2020. PMID: 31840624
-
Benzyl isothiocyanate (BITC) induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in human melanoma A375.S2 cells through reactive oxygen species (ROS) and both mitochondria-dependent and death receptor-mediated multiple signaling pathways.J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Jan 18;60(2):665-75. doi: 10.1021/jf204193v. Epub 2012 Jan 6. J Agric Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22148415
-
Therapeutic peptides: Targeting the mitochondrion to modulate apoptosis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Sep-Oct;1757(9-10):1312-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.07.002. Epub 2006 Jul 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16928356 Review.
-
Multifaceted roles of mitochondria in asthma.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Oct 9;40(1):85. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09928-8. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39382744 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bitter tastants relax the mouse gallbladder smooth muscle independent of signaling through tuft cells and bitter taste receptors.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 8;14(1):18447. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69287-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39117690 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of airway epithelial bitter taste receptors by Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolones modulates calcium, cyclic-AMP, and nitric oxide signaling.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jun 22;293(25):9824-9840. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001005. Epub 2018 May 10. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29748385 Free PMC article.
-
Ethylacetate extract from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial caspase-dependent intrinsic pathway in HepG2 cells.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jan;37(1):865-76. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3579-8. Epub 2015 Aug 9. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26254612
-
Emerging concepts in smooth muscle contributions to airway structure and function: implications for health and disease.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Dec 1;311(6):L1113-L1140. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00370.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27742732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Denatonium Benzoate-Induces Oxidative Stress in the Heart and Kidney of Chinese Fast Yellow Chickens by Regulating Apoptosis, Autophagy, Antioxidative Activities and Bitter Taste Receptor Gene Expressions.Animals (Basel). 2019 Sep 19;9(9):701. doi: 10.3390/ani9090701. Animals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31546822 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ogura T, Margolskee RF, Kinnamon SC. Taste receptor cell responses to the bitter stimulus denatonium involve Ca2+ influx via store-operated channels. J Neurophysiol. 2002;87:3152–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

