Development of chromosome-specific markers with high polymorphism for allotetraploid cotton based on genome-wide characterization of simple sequence repeats in diploid cottons (Gossypium arboreum L. and Gossypium raimondii Ulbrich)
- PMID: 25652321
- PMCID: PMC4325953
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-1265-2
Development of chromosome-specific markers with high polymorphism for allotetraploid cotton based on genome-wide characterization of simple sequence repeats in diploid cottons (Gossypium arboreum L. and Gossypium raimondii Ulbrich)
Abstract
Background: Tetraploid cotton contains two sets of homologous chromosomes, the At- and Dt-subgenomes. Consequently, many markers in cotton were mapped to multiple positions during linkage genetic map construction, posing a challenge to anchoring linkage groups and mapping economically-important genes to particular chromosomes. Chromosome-specific markers could solve this problem. Recently, the genomes of two diploid species were sequenced whose progenitors were putative contributors of the At- and Dt-subgenomes to tetraploid cotton. These sequences provide a powerful tool for developing chromosome-specific markers given the high level of synteny among tetraploid and diploid cotton genomes. In this study, simple sequence repeats (SSRs) on each chromosome in the two diploid genomes were characterized. Chromosome-specific SSRs were developed by comparative analysis and proved to distinguish chromosomes.
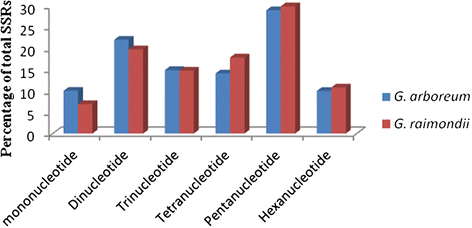
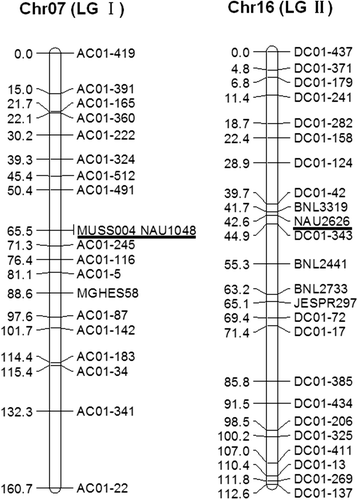
Results: A total of 200,744 and 142,409 SSRs were detected on the 13 chromosomes of Gossypium arboreum L. and Gossypium raimondii Ulbrich, respectively. Chromosome-specific SSRs were obtained by comparing SSR flanking sequences from each chromosome with those from the other 25 chromosomes. The average was 7,996 per chromosome. To confirm their chromosome specificity, these SSRs were used to distinguish two homologous chromosomes in tetraploid cotton through linkage group construction. The chromosome-specific SSRs and previously-reported chromosome markers were grouped together, and no marker mapped to another homologous chromosome, proving that the chromosome-specific SSRs were unique and could distinguish homologous chromosomes in tetraploid cotton. Because longer dinucleotide AT-rich repeats were the most polymorphic in previous reports, the SSRs on each chromosome were sorted by motif type and repeat length for convenient selection. The primer sequences of all chromosome-specific SSRs were also made publicly available.
Conclusion: Chromosome-specific SSRs are efficient tools for chromosome identification by anchoring linkage groups to particular chromosomes during genetic mapping and are especially useful in mapping of qualitative-trait genes or quantitative trait loci with just a few markers. The SSRs reported here will facilitate a number of genetic and genomic studies in cotton, including construction of high-density genetic maps, positional gene cloning, fingerprinting, and genetic diversity and comparative evolutionary analyses among Gossypium species.
Figures

References
-
- Hans E. Microsatellites: simple sequences with complex evolution. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:435–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

