Functional organization of excitatory synaptic strength in primary visual cortex
- PMID: 25652823
- PMCID: PMC4843963
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14182
Functional organization of excitatory synaptic strength in primary visual cortex
Abstract
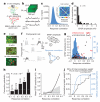
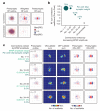
The strength of synaptic connections fundamentally determines how neurons influence each other's firing. Excitatory connection amplitudes between pairs of cortical neurons vary over two orders of magnitude, comprising only very few strong connections among many weaker ones. Although this highly skewed distribution of connection strengths is observed in diverse cortical areas, its functional significance remains unknown: it is not clear how connection strength relates to neuronal response properties, nor how strong and weak inputs contribute to information processing in local microcircuits. Here we reveal that the strength of connections between layer 2/3 (L2/3) pyramidal neurons in mouse primary visual cortex (V1) obeys a simple rule--the few strong connections occur between neurons with most correlated responses, while only weak connections link neurons with uncorrelated responses. Moreover, we show that strong and reciprocal connections occur between cells with similar spatial receptive field structure. Although weak connections far outnumber strong connections, each neuron receives the majority of its local excitation from a small number of strong inputs provided by the few neurons with similar responses to visual features. By dominating recurrent excitation, these infrequent yet powerful inputs disproportionately contribute to feature preference and selectivity. Therefore, our results show that the apparently complex organization of excitatory connection strength reflects the similarity of neuronal responses, and suggest that rare, strong connections mediate stimulus-specific response amplification in cortical microcircuits.
Figures
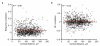

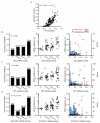
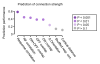
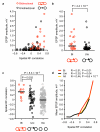
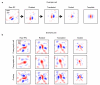
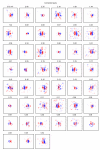
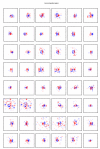
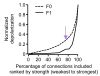
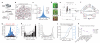

Comment in
-
Neuroscience: The cortical connection.Nature. 2015 Feb 19;518(7539):306-7. doi: 10.1038/nature14201. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25652821 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lefort S, Tomm C, Floyd Sarria J, Petersen CH. The excitatory neuronal network of the C2 barrel column in mouse primary somatosensory cortex. Neuron. 2009;61:301–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

