Influenza A M2 protein conformation depends on choice of model membrane
- PMID: 25652904
- PMCID: PMC4516663
- DOI: 10.1002/bip.22617
Influenza A M2 protein conformation depends on choice of model membrane
Abstract
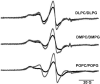
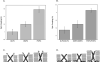
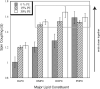
While crystal and NMR structures exist of the influenza A M2 protein, there is disagreement between models. Depending on the requirements of the technique employed, M2 has been studied in a range of membrane mimetics including detergent micelles and membrane bilayers differing in lipid composition. The use of different model membranes complicates the integration of results from published studies necessary for an overall understanding of the M2 protein. Here we show using site-directed spin-label EPR spectroscopy (SDSL-EPR) that the conformations of M2 peptides in membrane bilayers are clearly influenced by the lipid composition of the bilayers. Altering the bilayer thickness or the lateral pressure profile within the bilayer membrane changes the M2 conformation observed. The multiple M2 peptide conformations observed here, and in other published studies, optimistically may be considered conformations that are sampled by the protein at various stages during influenza infectivity. However, care should be taken that the heterogeneity observed in published structures is not simply an artifact of the choice of the model membrane.
Keywords: SDSL-EPR; hydrophobic mismatch; influenza A M2 protein; lateral pressure; model membrane; phosphatidylethanolamine; site-directed spin labeling.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

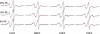
Similar articles
-
Helix tilt of the M2 transmembrane peptide from influenza A virus: an intrinsic property.J Mol Biol. 2000 Jan 7;295(1):117-25. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3322. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10623512
-
C-terminal juxtamembrane region of full-length M2 protein forms a membrane surface associated amphipathic helix.Protein Sci. 2015 Mar;24(3):426-9. doi: 10.1002/pro.2631. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Protein Sci. 2015. PMID: 25545360 Free PMC article.
-
Isotropic bicelles stabilize the juxtamembrane region of the influenza M2 protein for solution NMR studies.Biochemistry. 2013 Nov 26;52(47):8420-9. doi: 10.1021/bi401035m. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 24168642
-
Influence of solubilizing environments on membrane protein structures.Trends Biochem Sci. 2011 Feb;36(2):117-25. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2010.07.005. Epub 2010 Aug 18. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011. PMID: 20724162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
M2 protein from influenza A: from multiple structures to biophysical and functional insights.Curr Opin Virol. 2012 Apr;2(2):128-33. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2012.01.005. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Curr Opin Virol. 2012. PMID: 22482709 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Binding and Proton Blockage by Amantadine Variants of the Influenza M2WT and M2S31N Explained.J Med Chem. 2017 Mar 9;60(5):1716-1733. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01115. Epub 2017 Feb 15. J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28107633 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of Detergent-Mediated Reconstitution of Influenza A M2 Protein into Proteoliposomes.Membranes (Basel). 2018 Nov 8;8(4):103. doi: 10.3390/membranes8040103. Membranes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30413063 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol and M2 Rendezvous in Budding and Scission of Influenza A Virus.Subcell Biochem. 2023;106:441-459. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-40086-5_16. Subcell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 38159237
-
Structure and Dynamics of Membrane Proteins from Solid-State NMR.Annu Rev Biophys. 2018 May 20;47:201-222. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-070816-033712. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Annu Rev Biophys. 2018. PMID: 29498890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism and Kinetics of Copper Complexes Binding to the Influenza A M2 S31N and S31N/G34E Channels.Biophys J. 2021 Jan 5;120(1):168-177. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.11.016. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Biophys J. 2021. PMID: 33248127 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

