Influenza A M2 protein conformation depends on choice of model membrane
- PMID: 25652904
- PMCID: PMC4516663
- DOI: 10.1002/bip.22617
Influenza A M2 protein conformation depends on choice of model membrane
Abstract
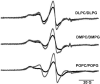
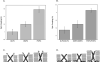
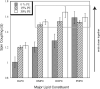
While crystal and NMR structures exist of the influenza A M2 protein, there is disagreement between models. Depending on the requirements of the technique employed, M2 has been studied in a range of membrane mimetics including detergent micelles and membrane bilayers differing in lipid composition. The use of different model membranes complicates the integration of results from published studies necessary for an overall understanding of the M2 protein. Here we show using site-directed spin-label EPR spectroscopy (SDSL-EPR) that the conformations of M2 peptides in membrane bilayers are clearly influenced by the lipid composition of the bilayers. Altering the bilayer thickness or the lateral pressure profile within the bilayer membrane changes the M2 conformation observed. The multiple M2 peptide conformations observed here, and in other published studies, optimistically may be considered conformations that are sampled by the protein at various stages during influenza infectivity. However, care should be taken that the heterogeneity observed in published structures is not simply an artifact of the choice of the model membrane.
Keywords: SDSL-EPR; hydrophobic mismatch; influenza A M2 protein; lateral pressure; model membrane; phosphatidylethanolamine; site-directed spin labeling.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

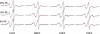
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

