Mechanisms and dynamics of AKAP79/150-orchestrated multi-protein signalling complexes in brain and peripheral nerve
- PMID: 25653013
- PMCID: PMC4704501
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.287698
Mechanisms and dynamics of AKAP79/150-orchestrated multi-protein signalling complexes in brain and peripheral nerve
Abstract
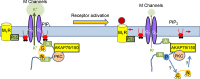
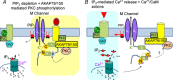
A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs) have emerged as a converging point of diverse signals to achieve spatiotemporal resolution of directed cellular regulation. With the extensive studies of AKAP79/150 in regulation of ion channel activity, the major questions to be posed centre on the mechanism and functional role of synergistic regulation of ion channels by such signalling proteins. In this review, we summarize recent discoveries of AKAP79/150-mediated modulation of voltage-gated neuronal M-type (KCNQ, Kv7) K(+) channels and L-type CaV 1 Ca(2+) channels, on both short- and longer-term time scales, highlighting the dynamics of the macromolecular signalling complexes in brain and peripheral nerve We also discuss several models for the possible mechanisms of these multi-protein assemblies and how they serve the agenda of the neurons in which they occur.
© 2015 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2015 The Physiological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ca2+/calmodulin disrupts AKAP79/150 interactions with KCNQ (M-Type) K+ channels.J Neurosci. 2010 Feb 10;30(6):2311-23. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5175-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20147557 Free PMC article.
-
AKAP79/150 signal complexes in G-protein modulation of neuronal ion channels.J Neurosci. 2011 May 11;31(19):7199-211. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4446-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21562284 Free PMC article.
-
Clustering and Functional Coupling of Diverse Ion Channels and Signaling Proteins Revealed by Super-resolution STORM Microscopy in Neurons.Neuron. 2016 Oct 19;92(2):461-478. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.09.014. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 27693258 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase C bound with A-kinase anchoring protein is involved in muscarinic receptor-activated modulation of M-type KCNQ potassium channels.Neurosci Res. 2005 Mar;51(3):231-4. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2004.11.009. Epub 2005 Jan 8. Neurosci Res. 2005. PMID: 15710486 Review.
-
A macromolecular trafficking complex composed of β₂-adrenergic receptors, A-Kinase Anchoring Proteins and L-type calcium channels.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2013 Jun;33(3):172-6. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2013.782219. Epub 2013 Apr 4. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2013. PMID: 23557075 Review.
Cited by
-
p85S6K sustains synaptic GluA1 to ameliorate cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease.Transl Neurodegener. 2023 Jan 9;12(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s40035-022-00334-w. Transl Neurodegener. 2023. PMID: 36624510 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-Associated Proteins in Neuroregeneration.Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 2;14(2):183. doi: 10.3390/biom14020183. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38397420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Localised intracellular signalling in neurons.J Physiol. 2016 Jan 1;594(1):7-8. doi: 10.1113/JP271357. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26724480 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
STIM2 targets Orai1/STIM1 to the AKAP79 signaling complex and confers coupling of Ca2+ entry with NFAT1 activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jul 14;117(28):16638-16648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1915386117. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32601188 Free PMC article.
-
Compartmentalized Signaling in Aging and Neurodegeneration.Cells. 2021 Feb 22;10(2):464. doi: 10.3390/cells10020464. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33671541 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Black DJ & Persechini A (2011). In calmodulin–IQ domain complexes, the Ca2+‐free and Ca2+‐bound forms of the calmodulin C‐lobe direct the N‐lobe to different binding sites. Biochemistry 50, 10061–10068. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

