Nascent transcription affected by RNA polymerase IV in Zea mays
- PMID: 25653306
- PMCID: PMC4391576
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.115.174714
Nascent transcription affected by RNA polymerase IV in Zea mays
Abstract
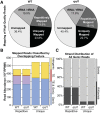
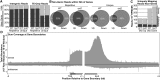
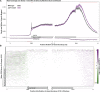
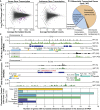
All eukaryotes use three DNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RNAPs) to create cellular RNAs from DNA templates. Plants have additional RNAPs related to Pol II, but their evolutionary role(s) remain largely unknown. Zea mays (maize) RNA polymerase D1 (RPD1), the largest subunit of RNA polymerase IV (Pol IV), is required for normal plant development, paramutation, transcriptional repression of certain transposable elements (TEs), and transcriptional regulation of specific alleles. Here, we define the nascent transcriptomes of rpd1 mutant and wild-type (WT) seedlings using global run-on sequencing (GRO-seq) to identify the broader targets of RPD1-based regulation. Comparisons of WT and rpd1 mutant GRO-seq profiles indicate that Pol IV globally affects transcription at both transcriptional start sites and immediately downstream of polyadenylation addition sites. We found no evidence of divergent transcription from gene promoters as seen in mammalian GRO-seq profiles. Statistical comparisons identify genes and TEs whose transcription is affected by RPD1. Most examples of significant increases in genic antisense transcription appear to be initiated by 3'-proximal long terminal repeat retrotransposons. These results indicate that maize Pol IV specifies Pol II-based transcriptional regulation for specific regions of the maize genome including genes having developmental significance.
Keywords: RNA polymerase IV; gene regulation; paramutation; transcription; transposons.
Copyright © 2015 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maize RNA PolIV affects the expression of genes with nearby TE insertions and has a genome-wide repressive impact on transcription.BMC Plant Biol. 2017 Oct 12;17(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1108-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 29025411 Free PMC article.
-
Maize RNA polymerase IV defines trans-generational epigenetic variation.Plant Cell. 2013 Mar;25(3):808-19. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.107680. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 23512852 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase IV functions in paramutation in Zea mays.Science. 2009 Feb 27;323(5918):1201-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1164508. Science. 2009. PMID: 19251626
-
Trans-Homolog Interactions Facilitating Paramutation in Maize.Plant Physiol. 2015 Aug;168(4):1226-36. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00591. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26149572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paramutation: a trans-homolog interaction affecting heritable gene regulation.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2012 Nov;15(5):536-43. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2012.09.003. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 23017240 Review.
Cited by
-
Stress-induced and epigenetic-mediated maize transcriptome regulation study by means of transcriptome reannotation and differential expression analysis.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 27;6:30446. doi: 10.1038/srep30446. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27461139 Free PMC article.
-
A matter of time - How transient transcription factor interactions create dynamic gene regulatory networks.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017 Jan;1860(1):75-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.08.007. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017. PMID: 27546191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cotranscriptional and Posttranscriptional Features of the Transcriptome in Soybean Shoot Apex and Leaf.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Apr 9;12:649634. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.649634. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33897737 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Methodologies in Studying lncRNAs in the High-Throughput Era: When Acronyms ATTACK!Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1933:1-30. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9045-0_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30945176 Free PMC article.
-
Locus-specific paramutation in Zea mays is maintained by a PICKLE-like chromodomain helicase DNA-binding 3 protein controlling development and male gametophyte function.PLoS Genet. 2020 Dec 15;16(12):e1009243. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009243. eCollection 2020 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 33320854 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alleman M., Sidorenko L., McGinnis K., Seshadri V., Dorweiler J. E., et al. , 2006. An RNA-dependent RNA polymerase is required for paramutation in maize. Nature 442: 295–298. - PubMed
-
- Ariel F., Jegu T., Latrasse D., Romero-Barrios N., Christ A., et al. , 2014. Noncoding transcription by alternative RNA polymerases dynamically regulates an auxin-driven chromatin loop. Mol. Cell 55: 383–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

