ATP1A1-mediated Src signaling inhibits coronavirus entry into host cells
- PMID: 25653449
- PMCID: PMC4442369
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.03274-14
ATP1A1-mediated Src signaling inhibits coronavirus entry into host cells
Abstract
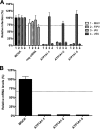
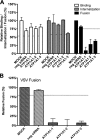
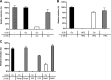
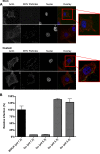
In addition to transporting ions, the multisubunit Na(+),K(+)-ATPase also functions by relaying cardiotonic steroid (CTS)-binding-induced signals into cells. In this study, we analyzed the role of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase and, in particular, of its ATP1A1 α subunit during coronavirus (CoV) infection. As controls, the vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) and influenza A virus (IAV) were included. Using gene silencing, the ATP1A1 protein was shown to be critical for infection of cells with murine hepatitis virus (MHV), feline infectious peritonitis virus (FIPV), and VSV but not with IAV. Lack of ATP1A1 did not affect virus binding to host cells but resulted in inhibited entry of MHV and VSV. Consistently, nanomolar concentrations of the cardiotonic steroids ouabain and bufalin, which are known not to affect the transport function of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase, inhibited infection of cells with MHV, FIPV, Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)-CoV, and VSV, but not IAV, when the compounds were present during virus inoculation. Cardiotonic steroids were shown to inhibit entry of MHV at an early stage, resulting in accumulation of virions close to the cell surface and, as a consequence, in reduced fusion. In agreement with an early block in infection, the inhibition of VSV by CTSs could be bypassed by low-pH shock. Viral RNA replication was not affected when these compounds were added after virus entry. The antiviral effect of ouabain could be relieved by the addition of different Src kinase inhibitors, indicating that Src signaling mediated via ATP1A1 plays a crucial role in the inhibition of CoV and VSV infections.
Importance: Coronaviruses (CoVs) are important pathogens of animals and humans, as demonstrated by the recent emergence of new human CoVs of zoonotic origin. Antiviral drugs targeting CoV infections are lacking. In the present study, we show that the ATP1A1 subunit of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase, an ion transporter and signaling transducer, supports CoV infection. Targeting ATP1A1 either by gene silencing or by low concentrations of the ATP1A1-binding cardiotonic steroids ouabain and bufalin resulted in inhibition of infection with murine, feline, and MERS-CoVs at an early entry stage. Infection with the control virus VSV was also inhibited. Src signaling mediated by ATP1A1 was shown to play a crucial role in the inhibition of virus entry by ouabain and bufalin. These results suggest that targeting the Na(+),K(+)-ATPase using cardiotonic steroids, several of which are FDA-approved compounds, may be an attractive therapeutic approach against CoV and VSV infections.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The alpha-1 subunit of the Na+,K+-ATPase (ATP1A1) is required for macropinocytic entry of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in human respiratory epithelial cells.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Aug 5;15(8):e1007963. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007963. eCollection 2019 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31381610 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiotonic steroids trigger non-classical testosterone signaling in Sertoli cells via the α4 isoform of the sodium pump.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Dec;1813(12):2118-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.07.012. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21820472
-
Natriuretic effect of bufalin in isolated rat kidneys involves activation of the Na+-K+-ATPase-Src kinase pathway.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Apr 15;302(8):F959-66. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00130.2011. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22237798
-
New insights into the regulation of Na+,K+-ATPase by ouabain.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2012;294:99-132. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394305-7.00002-1. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22364872 Review.
-
Endogenous and exogenous cardiac glycosides: their roles in hypertension, salt metabolism, and cell growth.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007 Aug;293(2):C509-36. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00098.2007. Epub 2007 May 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17494630 Review.
Cited by
-
Anticancer and Antiviral Properties of Cardiac Glycosides: A Review to Explore the Mechanism of Actions.Molecules. 2020 Aug 7;25(16):3596. doi: 10.3390/molecules25163596. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32784680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategy, Progress, and Challenges of Drug Repurposing for Efficient Antiviral Discovery.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 4;12:660710. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.660710. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34017257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review on potential of natural products in the management of COVID-19.RSC Adv. 2021 May 12;11(27):16711-16735. doi: 10.1039/d1ra00644d. eCollection 2021 Apr 30. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35479175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Alpha-1 Subunit of the Na+/K+-ATPase (ATP1A1) Is a Host Factor Involved in the Attachment of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 16;24(4):4000. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044000. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835408 Free PMC article.
-
Src-independent ERK signaling through the rat α3 isoform of Na/K-ATPase.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017 Mar 1;312(3):C222-C232. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00199.2016. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27903584 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

