Treatment of adult-onset Still's disease: a review
- PMID: 25653531
- PMCID: PMC4278737
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S64951
Treatment of adult-onset Still's disease: a review
Abstract
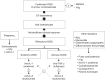
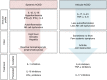
Adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) is a rare inflammatory disorder that has been recently classified as a polygenic autoinflammatory disorder. The former classification, based on the disease course, seems to be quite dated. Indeed, there is accumulating evidence that AOSD can be divided into two distinct phenotypes based on cytokine profile, clinical presentation, and outcome, ie, a "systemic" pattern and an "articular" pattern. The first part of this review deals with the treatments that are currently available for AOSD. We then present the different strategies based on the characteristics of the disease according to clinical presentation. To do so, we focus on the two subsets of the disease. Finally, we discuss the management of life-threatening complications of AOSD, along with the therapeutic options during pregnancy.
Keywords: adult-onset Still’s disease; anakinra; canakinumab; tocilizumab; treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Tanaka S, Matsumoto Y, Ohnishi H, et al. Comparison of clinical features of childhood and adult onset Still’s disease. Ryūmachi Rheum. 1991;31(5):511–518. Japanese. - PubMed
-
- Uppal SS, Pande IR, Kumar A, et al. Adult onset Still’s disease in northern India: comparison with juvenile onset Still’s disease. Br J Rheumatol. 1995;34(5):429–434. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

