Real-world effectiveness of amlodipine/valsartan and amlodipine/valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide in high-risk patients and other subgroups
- PMID: 25653536
- PMCID: PMC4309775
- DOI: 10.2147/VHRM.S76599
Real-world effectiveness of amlodipine/valsartan and amlodipine/valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide in high-risk patients and other subgroups
Abstract
Background: The clinical EXCITE (EXperienCe of amlodIpine and valsarTan in hypErtension) study reported clinically relevant blood pressure (BP) reductions across all doses of amlodipine/valsartan (Aml/Val) and Aml/Val/hydrochlorothiazide (HCT) single-pill combinations. The study prospectively observed a multiethnic population of hypertensive patients for 26 weeks who were treated according to routine clinical practice. Here, we present the results in high-risk subgroups including the elderly, obese patients, and patients with diabetes or isolated systolic hypertension. In addition, we present a post hoc analysis as per prior antihypertensive monotherapy and dual therapy.
Methods: Patients prescribed Aml/Val or Aml/Val/HCT were assessed in this 26±8 week, noninterventional, multicenter study across 13 countries in the Middle East and Asia. Changes in mean sitting systolic BP, mean sitting diastolic BP, and overall safety were assessed.
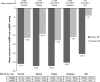
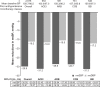
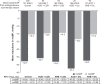
Results: Of a total of 9,794 patients analyzed, 8,603 and 1,191 patients were prescribed Aml/Val and Aml/Val/HCT, respectively. Among these, 15.5% were elderly, 32.5% were obese, 31.3% had diabetes, and 9.8% had isolated systolic hypertension. Both Aml/Val and Aml/Val/HCT single-pill combinations, respectively, were associated with clinically relevant and significant mean sitting systolic/diastolic BP reductions across all subgroups: elderly patients (-32.2/-14.3 mmHg and -38.5/-16.5 mmHg), obese patients (-32.2/-17.9 mmHg and -38.5/-18.4 mmHg), diabetic patients (-30.3/-16.1 mmHg and -34.4/-16.6 mmHg), and patients with isolated systolic hypertension (-25.5/-4.1 mmHg and -30.2/-5.9 mmHg). Incremental BP reductions with Aml/Val or Aml/Val/HCT single-pill combinations were also observed in patients receiving prior monotherapy or dual therapy for hypertension. Overall, both Aml/Val and Aml/Val/HCT were generally well tolerated.
Conclusion: This large, multiethnic study supports the evidence that Aml/Val and Aml/Val/ HCT single-pill combinations are effective in diverse and clinically important subgroups of patients with hypertension.
Keywords: amlodipine; hydrochlorothiazide; real world; single-pill combinations; valsartan.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Real-world clinical experience of amlodipine/valsartan and amlodipine/valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide in hypertension: the EXCITE study.Curr Med Res Opin. 2014 Oct;30(10):1937-45. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2014.942415. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014. PMID: 25007309
-
Real-life effectiveness, safety, and tolerability of amlodipine/valsartan or amlodipine/valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide single-pill combination in patients with hypertension from Pakistan.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2014 Apr;8(2):45-55. doi: 10.1177/1753944714525496. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2014. PMID: 24562476
-
Triple combination therapy with amlodipine, valsartan, and hydrochlorothiazide vs dual combination therapy with amlodipine and hydrochlorothiazide for stage 2 hypertensive patients.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2010 Sep 7;6:821-7. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.s11522. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2010. PMID: 20859551 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Amlodipine/valsartan single-pill combination: a review of its use in the management of hypertension.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2009;9(5):309-30. doi: 10.2165/11201120-000000000-00000. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19791840 Review.
-
Antihypertensive efficacy of olmesartan medoxomil or valsartan in combination with amlodipine: a review of factorial-design studies.Curr Med Res Opin. 2009 Jan;25(1):177-85. doi: 10.1185/03007990802597456. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009. PMID: 19210150 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Valsartan/Amlodipine Single-pill Combination in Hypertensive Patients With Excess Body Weight: Subanalysis of China Status II.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2015 Nov;66(5):497-503. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000301. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26248276 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–223. - PubMed
-
- Chow CK, Teo KK, Rangarajan S, et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in rural and urban communities in high-,middle-, and low-income countries. JAMA. 2013;310:959–968. - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, et al. 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) J Hypertens. 2013;31:1281–1357. - PubMed
-
- Bramlage P, Pittrow D, Wittchen HU, et al. Hypertension in overweight and obese primary care patients is highly prevalent and poorly controlled. Am J Hypertens. 2004;17:904–910. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

