Aggravation of hepatopulmonary syndrome after sildenafil treatment in a patient with coexisting portopulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 25653708
- PMCID: PMC4310984
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2015.45.1.77
Aggravation of hepatopulmonary syndrome after sildenafil treatment in a patient with coexisting portopulmonary hypertension
Abstract
Hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) and portopulmonary hypertension (PPHTN) are complications of portal hypertension and cirrhosis. Their pathophysiological mechanisms clearly differ. HPS is characterized by a defect in arterial oxygenation induced by pulmonary vascular dilatation. In contrast, PPHTN is predominantly due to excessive pulmonary vasoconstriction and vascular remodeling, but is rarely associated with hypoxia. We report a case of a patient who had both HPS and PPHTN at the time of presentation. HPS was aggravated after sildenafil administration for the treatment of PPHTN. We demonstrated increased amount of intrapulmonay shunt after sildenafil challenge by using agitated saline contrast transthoracic echocardiography.
Keywords: Hepatopulmonary syndrome; Pulmonary arterial hypertension; Sildenafil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
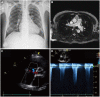
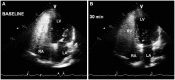
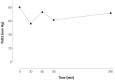
Similar articles
-
Hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension.Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2007 Apr;9(2):127-36. doi: 10.1007/s11936-007-0006-5. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2007. PMID: 17484815
-
Coexisting hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension: implications for liver transplantation.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010 Aug;44(7):e136-40. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181da76fc. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20463591
-
Transition from hepatopulmonary syndrome to portopulmonary hypertension: a case series of 3 patients.Case Rep Pulmonol. 2013;2013:561870. doi: 10.1155/2013/561870. Epub 2013 Nov 10. Case Rep Pulmonol. 2013. PMID: 24324910 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension: what's new?Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2007 Apr-Jun;70(2):203-9. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2007. PMID: 17715635 Review.
-
Late complications of biliary atresia: hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension.Pediatr Surg Int. 2017 Dec;33(12):1335-1340. doi: 10.1007/s00383-017-4176-2. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Pediatr Surg Int. 2017. PMID: 28983709 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanical characteristics of the pulmonary artery in beagle dogs with hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension.Biomed Rep. 2016 Jan;4(1):51-54. doi: 10.3892/br.2015.526. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Biomed Rep. 2016. PMID: 26870333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoeper MM, Krowka MJ, Strassburg CP. Portopulmonary hypertension and hepatopulmonary syndrome. Lancet. 2004;363:1461–1468. - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez-Roisin R, Krowka MJ. Hepatopulmonary syndrome--a liver-induced lung vascular disorder. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2378–2387. - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez-Roisin R, Krowka MJ, Hervé P, et al. Pulmonary-Hepatic vascular Disorders (PHD) Eur Respir J. 2004;24:861–880. - PubMed
-
- Pham DM, Subramanian R, Parekh S. Coexisting hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension: implications for liver transplantation. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;44:e136–e140. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

