Effect of pilocarpine on the formalin-induced orofacial pain in rats
- PMID: 25653753
- PMCID: PMC4312802
Effect of pilocarpine on the formalin-induced orofacial pain in rats
Abstract
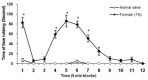
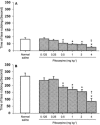
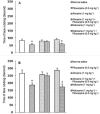
In this study, the effects of subcutaneous (SC) injection of pilocarpine (a cholinomimetic agent) and atropine (a muscarinic receptors antagonist) were investigated on a tonic model of orofacial pain in rats. The contribution of the endogenous analgesic opioid system was assessed using naloxone (an opioid receptors antagonist). Tonic orofacial pain was induced by SC injection of a diluted formalin solution (1%, 50 μL) in the right upper lip, and the time spent face rubbing was measured in five min blocks for 1 h. Formalin induced a biphasic (first phase: 0-5 min and second phase: 15-35 min) pain response. Pilocarpine significantly (P < 0.05) suppressed both phases of orofacial pain. Atropine did not have any effect and naloxone non-significantly increased the intensity of pain when used alone. In the pre-injection examinations, atropine prevented, but naloxone did not reverse the antinociceptive effect of pilocarpine. The results indicated that SC injection of formalin in the orofacial region induced a marked biphasic pain. Pilocarpine via muscarinic cholinergic receptors produced antinociceptive effect in the orofacial formalin-induced pain. The endogenous opioid analgesic system may not have a role in pilocarpine-induced antinociception.
Keywords: Atropine; Naloxone; Orofacial pain; Pilocarpine; Rat.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of opioid system in verapamil-induced antinociception in a rat model of orofacial pain.Vet Res Forum. 2014 Winter;5(1):49-54. Vet Res Forum. 2014. PMID: 25568692 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between histamine and morphine at the level of the hippocampus in the formalin-induced orofacial pain in rats.Pharmacol Rep. 2011;63(2):423-32. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(11)70508-4. Pharmacol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21602597
-
Central H2 histaminergic and alpha-2 adrenergic receptors involvement in crocetin-induced antinociception in orofacial formalin pain in rats.Vet Res Forum. 2020 Summer;11(3):229-234. doi: 10.30466/vrf.2018.83779.2101. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Vet Res Forum. 2020. PMID: 33133459 Free PMC article.
-
The orofacial formalin test.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004 Apr;28(2):219-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2003.12.003. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004. PMID: 15172765 Review.
-
Peripherally Acting Opioids in Orofacial Pain.Front Neurosci. 2021 May 4;15:665445. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.665445. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34017236 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of opioid system in verapamil-induced antinociception in a rat model of orofacial pain.Vet Res Forum. 2014 Winter;5(1):49-54. Vet Res Forum. 2014. PMID: 25568692 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between Analgesic Effect of Nano and Conventional size of Zinc Oxide and Opioidergic System Activity in Animal Model of Acute Pain.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2014 Winter;5(1):80-7. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25436088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raboisson P, Dallel R. The orofacial formalin test. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004;28:219–226. - PubMed
-
- Clavelou P, Pajot J, Dallel R, et al. Application of the formalin test to the study of orofacial pain in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1989;103:349–353. - PubMed
-
- Pajot J, Ressot C, Ngom I, et al. Gonadectomy induces site-specific differences in nociception in rats. Pain. 2003;104:367–373. - PubMed
-
- Erfanparast A, Tamaddonfard E, Farshid AA, et al. Effect of microinjection of histamine into the dorsal hippocampus on the orofacial formalin-induced pain in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010;627:119–123. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
