Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of pomegranate (Punica granatum) on Eimeria papillata-induced infection in mice
- PMID: 25654088
- PMCID: PMC4310320
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/219670
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of pomegranate (Punica granatum) on Eimeria papillata-induced infection in mice
Abstract
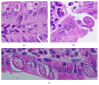
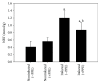
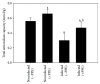
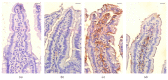
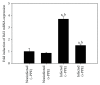
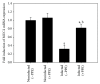
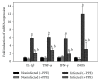
Coccidiosis is the most prevalent disease causing widespread economic loss, especially in poultry farms. Here, we investigated the effects of pomegranate peel extract (PPE) on the outcome of coccidiosis caused by Eimeria papillata in mice. The data showed that mice infected with E. papillata and treated with PPE revealed a significant decrease in the output of oocysts in their faeces by day 5 p.i. Infection also induced inflammation and injury of the jejunum. This was evidenced (i) as increases in reactive oxygen species, (ii), as increased neutrophils and decreased lymphocytes in blood (ii) as increased mRNA levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), Bcl-2 gene, and of the cytokines interferon gamma (IFN-γ), tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and (iv) as downregulation of mucin gene MUC2 mRNA. All these infection-induced parameters were significantly altered during PPE treatment. In particular, PPE counteracted the E. papillata-induced loss of the total antioxidant capacity. Our data indicated that PPE treatment significantly attenuated inflammation and injury of the jejunum induced by E. papillata infections.
Figures
References
-
- Mehlhorn H., Al-Quraishy S., Al-Rasheid K. A. S., Jatzlau A., Abdel-Ghaffar F. Addition of a combination of onion (Allium cepa) and coconut (Cocos nucifera) to food of sheep stops gastrointestinal helminthic infections. Parasitology Research. 2011;108(4):1041–1046. doi: 10.1007/s00436-010-2169-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

